Advancements in Testing Strategies for COVID-19
- PMID: 35735558
- PMCID: PMC9220779
- DOI: 10.3390/bios12060410
Advancements in Testing Strategies for COVID-19
Abstract
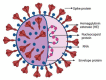
The SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus, also known as the disease-causing agent for COVID-19, is a virulent pathogen that may infect people and certain animals. The global spread of COVID-19 and its emerging variation necessitates the development of rapid, reliable, simple, and low-cost diagnostic tools. Many methodologies and devices have been developed for the highly sensitive, selective, cost-effective, and rapid diagnosis of COVID-19. This review organizes the diagnosis platforms into four groups: imaging, molecular-based detection, serological testing, and biosensors. Each platform's principle, advancement, utilization, and challenges for monitoring SARS-CoV-2 are discussed in detail. In addition, an overview of the impact of variants on detection, commercially available kits, and readout signal analysis has been presented. This review will expand our understanding of developing advanced diagnostic approaches to evolve into susceptible, precise, and reproducible technologies to combat any future outbreak.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; coronavirus; diagnosis; immunoassays; variants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

 ) to a quencher (
) to a quencher ( ). Mutant in the right graph showed a lower LOD (3-folds) than the wild in the left graph. (d) Colorimetric detection of SARS-CoV-2 by mutant N1 complex by a dye phenol red (a pH-sensitive dye) incubated at 60 °C for 30 min. (e) Visible fluorometric detection by the mutant N1 complex using calcein, incubated for 60 min at 60 °C [102].
). Mutant in the right graph showed a lower LOD (3-folds) than the wild in the left graph. (d) Colorimetric detection of SARS-CoV-2 by mutant N1 complex by a dye phenol red (a pH-sensitive dye) incubated at 60 °C for 30 min. (e) Visible fluorometric detection by the mutant N1 complex using calcein, incubated for 60 min at 60 °C [102].
Similar articles
-
Low-Cost Biosensor Technologies for Rapid Detection of COVID-19 and Future Pandemics.ACS Nano. 2024 Jan 23;18(3):1757-1777. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c01629. Epub 2024 Jan 8. ACS Nano. 2024. PMID: 38189684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel approaches for rapid detection of COVID-19 during the pandemic: A review.Anal Biochem. 2021 Dec 1;634:114362. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2021.114362. Epub 2021 Aug 31. Anal Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34478703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Diagnostic Tools for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2.Int Rev Immunol. 2021;40(1-2):143-156. doi: 10.1080/08830185.2020.1871477. Epub 2021 Jan 13. Int Rev Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33439059 Review.
-
Future developments in biosensors for field-ready SARS-CoV-2 virus diagnostics.Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2021 Aug;68(4):695-699. doi: 10.1002/bab.2033. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2021. PMID: 32970352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineered two-dimensional nanomaterials based diagnostics integrated with internet of medical things (IoMT) for COVID-19.Chem Soc Rev. 2024 Apr 22;53(8):3774-3828. doi: 10.1039/d3cs00719g. Chem Soc Rev. 2024. PMID: 38433614 Review.
Cited by
-
A Comparison Study of the Detection Limit of Omicron SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid by Various Rapid Antigen Tests.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 27;12(12):1083. doi: 10.3390/bios12121083. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551050 Free PMC article.
-
The COVID-19 inflammation and high mortality mechanism trigger.Immunogenetics. 2024 Feb;76(1):15-25. doi: 10.1007/s00251-023-01326-4. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Immunogenetics. 2024. PMID: 38063879 Review.
-
Comparison of a Blood Self-Collection System with Routine Phlebotomy for SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Testing.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Jul 31;12(8):1857. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12081857. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36010206 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2-on-Chip for Long COVID Management.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Oct 18;12(10):890. doi: 10.3390/bios12100890. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36291027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 and animals, a long story that doesn't have to end now: What we need to learn from the emergence of the Omicron variant.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Dec 15;9:1085613. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.1085613. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36590812 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Peiris J.S.M. Coronaviruses. In: Greenwood D., Barer M., Slack R., Irving W., editors. Medical Microbiology (Eighteenth Edition) Churchill Livingstone; Edinburgh, UK: 2012. pp. 587–593.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

