The Time-Dependent Role of Bisphosphonates on Atherosclerotic Plaque Calcification
- PMID: 35735797
- PMCID: PMC9225625
- DOI: 10.3390/jcdd9060168
The Time-Dependent Role of Bisphosphonates on Atherosclerotic Plaque Calcification
Abstract
Atherosclerotic plaque calcification directly contributes to the leading cause of morbidity and mortality by affecting plaque vulnerability and rupture risk. Small microcalcifications can increase plaque stress and promote rupture, whereas large calcifications can stabilize plaques. Drugs that target bone mineralization may lead to unintended consequences on ectopic plaque calcification and cardiovascular outcomes. Bisphosphonates, common anti-osteoporotic agents, have elicited unexpected cardiovascular events in clinical trials. Here, we investigated the role of bisphosphonate treatment and timing on the disruption or promotion of vascular calcification and bone minerals in a mouse model of atherosclerosis. We started the bisphosphonate treatment either before plaque formation, at early plaque formation times associated with the onset of calcification, or at late stages of plaque development. Our data indicated that long-term bisphosphonate treatment (beginning prior to plaque development) leads to higher levels of plaque calcification, with a narrower mineral size distribution. When given later in plaque development, we measured a wider distribution of mineral size. These morphological alterations might be associated with a higher risk of plaque rupture by creating stress foci. Yet, bone mineral density positively correlated with the duration of the bisphosphonate treatment.
Keywords: atherosclerotic plaque calcification; bisphosphonates; calcification paradox.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


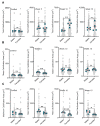


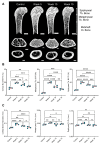
References
-
- Ruiz J.L., Hutcheson J.D., Cardoso L., Bakhshian Nik A., Condado de Abreu A., Pham T., Buffolo F., Busatto S., Federici S., Ridolfi A., et al. Nanoanalytical analysis of bisphosphonate-driven alterations of microcalcifications using a 3D hydrogel system and in vivo mouse model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2021;118:e1811725118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1811725118. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Peng A.W., Mirbolouk M., Orimoloye O.A., Osei A.D., Dardari Z., Dzaye O., Budoff M.J., Shaw L., Miedema M.D., Rumberger J., et al. Long-Term All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality in Asymptomatic Patients with CAC ≥ 1000. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging. 2020;13:83–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2019.02.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

