Post-Translational Modifications of PCNA: Guiding for the Best DNA Damage Tolerance Choice
- PMID: 35736104
- PMCID: PMC9225081
- DOI: 10.3390/jof8060621
Post-Translational Modifications of PCNA: Guiding for the Best DNA Damage Tolerance Choice
Abstract
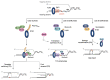
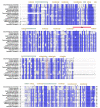
The sliding clamp PCNA is a multifunctional homotrimer mainly linked to DNA replication. During this process, cells must ensure an accurate and complete genome replication when constantly challenged by the presence of DNA lesions. Post-translational modifications of PCNA play a crucial role in channeling DNA damage tolerance (DDT) and repair mechanisms to bypass unrepaired lesions and promote optimal fork replication restart. PCNA ubiquitination processes trigger the following two main DDT sub-pathways: Rad6/Rad18-dependent PCNA monoubiquitination and Ubc13-Mms2/Rad5-mediated PCNA polyubiquitination, promoting error-prone translation synthesis (TLS) or error-free template switch (TS) pathways, respectively. However, the fork protection mechanism leading to TS during fork reversal is still poorly understood. In contrast, PCNA sumoylation impedes the homologous recombination (HR)-mediated salvage recombination (SR) repair pathway. Focusing on Saccharomyces cerevisiae budding yeast, we summarized PCNA related-DDT and repair mechanisms that coordinately sustain genome stability and cell survival. In addition, we compared PCNA sequences from various fungal pathogens, considering recent advances in structural features. Importantly, the identification of PCNA epitopes may lead to potential fungal targets for antifungal drug development.
Keywords: DNA damage tolerance; DNA replication forks; DNA replication stress; PCNA; fungal genome stability; post-translational modifications; salvage recombination; template switch; translesion synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

