Purification and Characterization of a Novel α-L-Rhamnosidase from Papiliotrema laurentii ZJU-L07 and Its Application in Production of Icariin from Epimedin C
- PMID: 35736128
- PMCID: PMC9225045
- DOI: 10.3390/jof8060644
Purification and Characterization of a Novel α-L-Rhamnosidase from Papiliotrema laurentii ZJU-L07 and Its Application in Production of Icariin from Epimedin C
Abstract
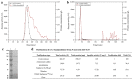
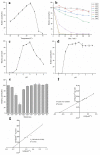
Icariin is the most effective bioactive compound in Herba Epimedii. To enhance the content of icariin in the epimedium water extract, a novel strain, Papiliotrema laurentii ZJU-L07, producing an intracellular α-L-rhamnosidase was isolated from the soil and mutagenized. The specific activity of α-L-rhamnosidase was 29.89 U·mg-1 through purification, and the molecular mass of the enzyme was 100 kDa, as assayed by SDS-PAGE. The characterization of the purified enzyme was determined. The optimal temperature and pH were 55 °C and 7.0, respectively. The enzyme was stable in the pH range 5.5-9.0 for 2 h over 80% and the temperature range 30-40 °C for 2 h more than 70%. The enzyme activity was inhibited by Ca2+, Fe2+, Cu2+, and Mg2+, especially Fe2+. The kinetic parameters of Km and Vmax were 1.38 mM and 24.64 μmol·mg-1·min-1 using pNPR as the substrate, respectively. When epimedin C was used as a nature substrate to determine the kinetic parameters of α-L-rhamnosidase, the values of Km and Vmax were 3.28 mM and 0.01 μmol·mg-1·min-1, respectively. The conditions of enzymatic hydrolysis were optimized through single factor experiments and response surface methodology. The icariin yield increased from 61% to over 83% after optimization. The enzymatic hydrolysis method could be used for the industrialized production of icariin. At the same time, this enzyme could also cleave the α-1,2 glycosidic linkage between glucoside and rhamnoside in naringin and neohesperidin, which could be applicable in other biotechnological processes.
Keywords: Papiliotrema laurentii ZJU-L07; enzyme characteristics; epimedin C; icariin; optimization; α-L-rhamnosidase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Jiang J., Song J., Jia X.-B. Phytochemistry and Ethnopharmacology of Epimedium L. Species. Chin. Herb. Med. 2015;7:204–222. doi: 10.1016/S1674-6384(15)60043-0. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

