Phytochemical and Potential Properties of Seaweeds and Their Recent Applications: A Review
- PMID: 35736145
- PMCID: PMC9227187
- DOI: 10.3390/md20060342
Phytochemical and Potential Properties of Seaweeds and Their Recent Applications: A Review
Abstract
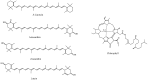
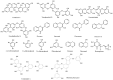
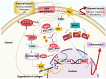
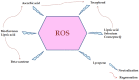
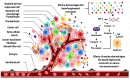
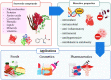
Since ancient times, seaweeds have been employed as source of highly bioactive secondary metabolites that could act as key medicinal components. Furthermore, research into the biological activity of certain seaweed compounds has progressed significantly, with an emphasis on their composition and application for human and animal nutrition. Seaweeds have many uses: they are consumed as fodder, and have been used in medicines, cosmetics, energy, fertilizers, and industrial agar and alginate biosynthesis. The beneficial effects of seaweed are mostly due to the presence of minerals, vitamins, phenols, polysaccharides, and sterols, as well as several other bioactive compounds. These compounds seem to have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, antimicrobial, and anti-diabetic activities. Recent advances and limitations for seaweed bioactive as a nutraceutical in terms of bioavailability are explored in order to better comprehend their therapeutic development. To further understand the mechanism of action of seaweed chemicals, more research is needed as is an investigation into their potential usage in pharmaceutical companies and other applications, with the ultimate objective of developing sustainable and healthier products. The objective of this review is to collect information about the role of seaweeds on nutritional, pharmacological, industrial, and biochemical applications, as well as their impact on human health.
Keywords: antioxidant activity; functional foods; health benefits; seaweeds; secondary metabolites.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
An Overview of Potential Seaweed-Derived Bioactive Compounds for Pharmaceutical Applications.Mar Drugs. 2022 Feb 15;20(2):141. doi: 10.3390/md20020141. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35200670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Seaweed as a source of novel nutraceuticals: sulfated polysaccharides and peptides.Adv Food Nutr Res. 2011;64:325-37. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-387669-0.00026-0. Adv Food Nutr Res. 2011. PMID: 22054959 Review.
-
Bioactive Compounds of Marine Algae and Their Potential Health and Nutraceutical Applications: A Review.Mar Drugs. 2025 Mar 31;23(4):152. doi: 10.3390/md23040152. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40278274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioactive polysaccharides from red seaweed as potent food supplements: a systematic review of their extraction, purification, and biological activities.Carbohydr Polym. 2022 Jan 1;275:118696. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118696. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Carbohydr Polym. 2022. PMID: 34742423
-
Environmental Impact on Seaweed Phenolic Production and Activity: An Important Step for Compound Exploitation.Mar Drugs. 2021 Apr 26;19(5):245. doi: 10.3390/md19050245. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33926129 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Optimization of fucoxanthin extraction obtained from natural by-products from Undaria pinnatifida stem using supercritical CO2 extraction method.Front Nutr. 2022 Sep 29;9:981176. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.981176. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36245524 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Review on Nutraceuticals: Therapy Support and Formulation Challenges.Nutrients. 2022 Nov 3;14(21):4637. doi: 10.3390/nu14214637. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36364899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutritional composition and phenolic contents of Gracilariopsis longissima, Padina tetrastromatica and Ulva intestinalis from the Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh coast.Heliyon. 2024 May 11;10(10):e31128. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31128. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38778999 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Polyphenols and Other Micronutrients of Marine Origin.Mar Drugs. 2023 May 26;21(6):323. doi: 10.3390/md21060323. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37367648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cognitive and anti-inflammatory effects of Palmaria palmata in a schizophrenia mouse model: insights into CREB signaling, Iba-1 expression, and CD4+ cell modulation.Front Neurosci. 2025 Jun 4;19:1551764. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1551764. eCollection 2025. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40535971 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Duarte C.M., Marbá N., Holmer M. Rapid domestication of marine species. [(accessed on 20 April 2007)];Science. 2007 316:382–383. doi: 10.1126/science.1138042. Available online: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.1138042. - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Irkin L.C., Yayintas Ö. Pharmacological Properties and Therapeutic Benefits of Seaweeds (A Review) Int. J. Trend Sci. Res. Dev. 2018;2:1126–1131. doi: 10.31142/ijtsrd9567. - DOI
-
- Chapman V.J., Chapman D.J. Seaweeds and Their Uses. 3rd ed. Chapman and Hall in Associate with Methuen; London, UK: 1980. p. 334. - DOI
-
- Vieira E.F., Soares C., Machado S., Correia M., Ramalhosa M.J., Oliva-Teles M.T., Paula Carvalho A., Domingues V.F., Antunes F., Oliveira T.A.C., et al. Seaweeds from the Portuguese coast as a source of proteinaceous material: Total and free amino acid composition profile. Food Chem. 2018;269:264–275. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.06.145. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

