Antiviral Activity and Mechanisms of Seaweeds Bioactive Compounds on Enveloped Viruses-A Review
- PMID: 35736188
- PMCID: PMC9228758
- DOI: 10.3390/md20060385
Antiviral Activity and Mechanisms of Seaweeds Bioactive Compounds on Enveloped Viruses-A Review
Abstract
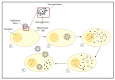
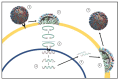
In the last decades, the interest in seaweed has significantly increased. Bioactive compounds from seaweed's currently receive major attention from pharmaceutical companies as they express several interesting biological activities which are beneficial for humans. The structural diversity of seaweed metabolites provides diverse biological activities which are expressed through diverse mechanisms of actions. This review mainly focuses on the antiviral activity of seaweed's extracts, highlighting the mechanisms of actions of some seaweed molecules against infection caused by different types of enveloped viruses: influenza, Lentivirus (HIV-1), Herpes viruses, and coronaviruses. Seaweed metabolites with antiviral properties can act trough different pathways by increasing the host's defense system or through targeting and blocking virus replication before it enters host cells. Several studies have already established the large antiviral spectrum of seaweed's bioactive compounds. Throughout this review, antiviral mechanisms and medical applications of seaweed's bioactive compounds are analyzed, suggesting seaweed's potential source of antiviral compounds for the formulation of novel and natural antiviral drugs.
Keywords: HIV; HSV; IAV; antiviral activity; enveloped virus; polyphenol; polysaccharide; seaweed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel Technologies for Seaweed Polysaccharides Extraction and Their Use in Food with Therapeutically Applications-A Review.Foods. 2022 Sep 1;11(17):2654. doi: 10.3390/foods11172654. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36076839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Overview of Potential Seaweed-Derived Bioactive Compounds for Pharmaceutical Applications.Mar Drugs. 2022 Feb 15;20(2):141. doi: 10.3390/md20020141. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35200670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overview on the antiviral activities and mechanisms of marine polysaccharides from seaweeds.Carbohydr Res. 2017 Dec 1;453-454:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2017.10.020. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Carbohydr Res. 2017. PMID: 29102716 Review.
-
From Ocean to Medicine: Harnessing Seaweed's Potential for Drug Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 8;25(2):797. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020797. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38255871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Seaweed's Bioactive Candidate Compounds to Food Industry and Global Food Security.Life (Basel). 2020 Aug 6;10(8):140. doi: 10.3390/life10080140. Life (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32781632 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Technologies for Seaweed Polysaccharides Extraction and Their Use in Food with Therapeutically Applications-A Review.Foods. 2022 Sep 1;11(17):2654. doi: 10.3390/foods11172654. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36076839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fucoidans of Brown Algae: Comparison of Sulfated Polysaccharides from Fucus vesiculosus and Ascophyllum nodosum.Mar Drugs. 2022 Oct 13;20(10):638. doi: 10.3390/md20100638. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36286461 Free PMC article.
-
Polysaccharides from the Sargassum and Brown Algae Genus: Extraction, Purification, and Their Potential Therapeutic Applications.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jun 25;12(13):2445. doi: 10.3390/plants12132445. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37447006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Seaweed for climate mitigation, wastewater treatment, bioenergy, bioplastic, biochar, food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics: a review.Environ Chem Lett. 2023;21(1):97-152. doi: 10.1007/s10311-022-01520-y. Epub 2022 Oct 8. Environ Chem Lett. 2023. PMID: 36245550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiviral Activity of Kappaphycus alvarezii Seaweed against ZIKV.Curr Top Med Chem. 2024;24(18):1589-1598. doi: 10.2174/0115680266294503240513044930. Curr Top Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38797894
References
-
- Jabłonowska E., Pulik P., Kalinowska A., Gąsiorowski J., Parczewski M., Bociąga-Jasik M., Pulik Ł., Siwak E., Wójcik K. Efficacy and safety of nucleoside-sparing regimen based on raltegravir and ritonavir-boosted darunavir in HIV-1-infected treatment-experienced patients. J. Med. Virol. 2017;89:2122–2129. doi: 10.1002/jmv.24826. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

