Influence of the Zeolite ZSM-22 Precursor on a UF-PES Selective Substrate Layer for Salts Rejection
- PMID: 35736260
- PMCID: PMC9230752
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes12060553
Influence of the Zeolite ZSM-22 Precursor on a UF-PES Selective Substrate Layer for Salts Rejection
Abstract
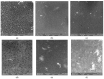
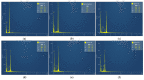
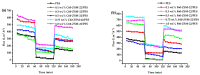
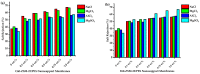
Fabrication of the ZSM-22/Polyethersulfone (ZSM-22/PES) membranes as selective salt filters represent a growing membrane technological area in separation with the potential of high economic reward based on its low energy requirements. The incorporation of ZSM-22 zeolite material as additives into the PES polymer matrix has the prospective advantage of combining both the zeolite and polymer features while overcoming the limitations associated with both materials. This work investigated the influence of the nature of the silica precursor on ZSM-22 zeolite hydrothermally synthesised using colloidal (C60) and fumed (C60) silica to Si/Al of 60. The successful synthesis of the highly crystalline zeolitic materials was confirmed through XRD, FTIR, and SEM with EDX. The ZSM-22 additives were directly dispersed into a PES polymeric matrix to form a casting solution for the preparation of the ZSM-22/PES selective substrate layers via a phase inversion method for salts rejection. The polymeric PES was selected as an organic network in which the content of the ZSM-22 zeolite (ranging between 0 and 1.0 wt.%), was obtained and characterised by XRD, FTIR, and SEM analysis, as well as water contact angle (WCA) measurement and dead-end filtration cell. The phase inversion preparation method has induced the resulting ZSM-22/PES NF substrates anisotropy, as attributed to a high water flux to the above 700 L·m-2·h-1; high selectivity and rejection of salts to above 80% is revealed by the obtained results. The materials also exhibited improved antifouling behavior to above 70% flux recovery ratios. As such, the nature of the silica precursor influences ZSM-22 zeolite synthesis as a potential additive in the PES polymer matrix and led to the enhanced performance of the pure PES ultrafiltration membrane.
Keywords: membrane preparation; membrane separation; nanocomposite membranes; nanofiltration membrane; polymeric membranes; zeolite ZSM-22 materials.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict to declare.
Figures











Similar articles
-
Development of ZSM-22/Polyethersulfone Membrane for Effective Salt Rejection.Polymers (Basel). 2020 Jun 28;12(7):1446. doi: 10.3390/polym12071446. Polymers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32605204 Free PMC article.
-
Pervaporation separation of ethyl acetate from aqueous solutions using ZSM-5 filled dual-layer poly(ether-block-amide)/polyethersulfone membrane.RSC Adv. 2018 Jan 26;8(9):4713-4725. doi: 10.1039/c7ra13382k. eCollection 2018 Jan 24. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35539544 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of monomers involved in the fabrication of a novel PES based nanofiltration thin-film composite membrane and its performance in the treatment of common effluent (CETP) textile industrial wastewater.J Environ Health Sci Eng. 2021 Mar 16;19(1):515-529. doi: 10.1007/s40201-021-00624-x. eCollection 2021 Jun. J Environ Health Sci Eng. 2021. PMID: 34150255 Free PMC article.
-
State-of-the-Art of Polymer/Fullerene C60 Nanocomposite Membranes for Water Treatment: Conceptions, Structural Diversity and Topographies.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Dec 25;13(1):27. doi: 10.3390/membranes13010027. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36676834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in hydrophilic modification and performance of polyethersulfone (PES) membrane via additive blending.RSC Adv. 2018 Jun 20;8(40):22710-22728. doi: 10.1039/c8ra03296c. eCollection 2018 Jun 19. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35539743 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mavukkandy M.O., Chabib C.M., Mustafa I., Al Ghaferi A., AlMarzooqi F. Brine management in desalination industry: From waste to resources generation. Desalination. 2019;472:114187. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2019.114187. - DOI
-
- Kucera J. Desalination: Water from Water. John Wiley & Sons; New York, NY, USA: 2019.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

