Negatively Charged MOF-Based Composite Anion Exchange Membrane with High Cation Selectivity and Permeability
- PMID: 35736308
- PMCID: PMC9227639
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes12060601
Negatively Charged MOF-Based Composite Anion Exchange Membrane with High Cation Selectivity and Permeability
Abstract
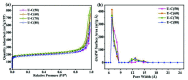
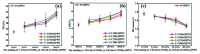
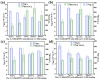
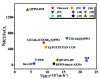
Every metal and metallurgical industry is associated with the generation of wastewater, influencing the living and non-living environment, which is alarming to environmentalists. The strict regulations about the dismissal of acid and metal into the environment and the increasing emphasis on the recycling/reuse of these effluents after proper remedy have focused the research community's curiosity in developing distinctive approaches for the recovery of acid and metals from industrial wastewaters. This study reports the synthesis of UiO-66-(COOH)2 using dual ligand in water as a green solvent. Then, the prepared MOF nanoparticles were introduced into the DMAM quaternized QPPO matrix through a straightforward blending approach. Four defect-free UiO-66-(COOH)2/QPPO MMMs were prepared with four different MOF structures. The BET characterization of UiO-66-(COOH)2 nanoparticles with a highly crystalline structure and sub-nanometer pore size (~7 Å) was confirmed by XRD. Because of the introduction of MOF nanoparticles with an electrostatic interaction and pore size screening effect, a separation coefficient (SHCl/FeCl2) of 565 and UHCl of 0.0089 m·h-1 for U-C(60)/QPPO were perceived when the loading dosage of the MOF content was 10 wt%. The obtained results showed that the prepared defect-free MOF membrane has broad prospects in acid recovery applications.
Keywords: UiO-66; acid recovery; cation separation; diffusive dialysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Zirconium-Based Nanoscale Metal-Organic Framework/Poly(ε-caprolactone) Mixed-Matrix Membranes as Effective Antimicrobials.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017 Nov 29;9(47):41512-41520. doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b15826. Epub 2017 Nov 16. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017. PMID: 29115828
-
The assessment of honeycomb structure UiO-66 and amino functionalized UiO-66 metal-organic frameworks to modify the morphology and performance of Pebax®1657-based gas separation membranes for CO2 capture applications.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Nov;27(32):40618-40632. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09927-2. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32671703
-
Defect-Free MOF-Based Mixed-Matrix Membranes Obtained by Corona Cross-Linking.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019 Apr 3;11(13):13029-13037. doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b02539. Epub 2019 Mar 21. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019. PMID: 30855936
-
An overview of the recovery of acid from spent acidic solutions from steel and electroplating industries.J Hazard Mater. 2009 Nov 15;171(1-3):61-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.06.099. Epub 2009 Jun 25. J Hazard Mater. 2009. PMID: 19632040 Review.
-
Diffusion Dialysis for Acid Recovery from Acidic Waste Solutions: Anion Exchange Membranes and Technology Integration.Membranes (Basel). 2020 Jul 29;10(8):169. doi: 10.3390/membranes10080169. Membranes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32751246 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- López J., de Oliveira R., Reig M., Vecino X., Gibert O., de Juan A., Cortina J. Acid recovery from copper metallurgical process streams polluted with arsenic by diffusion dialysis. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021;9:104692. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2020.104692. - DOI
-
- Wang P., Wang P., Guo Y., Rao L., Yan C. Selective recovery of protonated dyes from dye wastewater by pH-responsive BCN material. Chem. Eng. J. 2021;412:128532. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.128532. - DOI
-
- Jallouli W., Keskes S., Guidara W., Rezgui F., Sayadi S., Tounsi S. Membrane distillation and dispersive solvent extraction in a closed-loop process for water, sulfuric acid and copper recycling from gold mining wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2022;435:133874.
-
- Yang C.-C., Pan J., Zhu D.-Q., Guo Z.-Q., Li X.-M. Pyrometallurgical recycling of stainless-steel pickling sludge: A review. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2019;26:547–557. doi: 10.1007/s42243-019-00278-y. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

