Protective Effect of Butanolic Fraction of Delphinium brunonianum on Fructose-Mediated Metabolic Alterations in Rats
- PMID: 35736413
- PMCID: PMC9227329
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo12060481
Protective Effect of Butanolic Fraction of Delphinium brunonianum on Fructose-Mediated Metabolic Alterations in Rats
Abstract
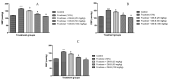
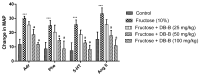
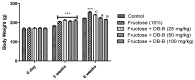
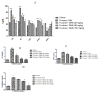
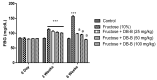
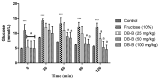
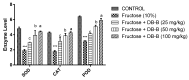
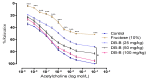
The present study was conducted with an intent to evaluate the protective effect of butanolic fraction of Delphinium brunonianum on fructose mediated metabolic abnormalities in rats. Rats in all groups except control group were fed on 10% fructose for 6 weeks; however, rats in the treated group also received butanolic fraction for the last 3 weeks, along with the fructose. Moreover, phytoconstituents present in butanolic fraction were analyzed using LC-MS. All doses of butanolic fraction profoundly reduce the fructose-induced blood pressure, sympathetic over-activity, and weight gain. Furthermore, butanolic fraction prominently reduces the glucose intolerance and hyperinsulinemia in fructose-fed rats. On treatment with butanolic fraction, oxidative enzymes and the functionality of the aorta was also restored. Phytochemical analysis revealed the presence of several active constituents including bergenin, scopolin, rutinoside, kaempferol, coumaric acid, apigenin, and gingerol. In conclusion, butanolic fraction of Delphinium brunonianum has the potential to prevent and recover the fructose-induced metabolic perturbations.
Keywords: LC-MS analysis; insulin resistance; metabolic syndrome; oxidative stress; sympathetic over-activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
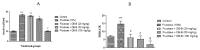
Similar articles
-
Phytochemical analysis of crude extract of Delphinium brunonianum and its effect on hypertension and metabolic perturbations in fructose fed rats.Nat Prod Res. 2021 Sep;35(17):2982-2986. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2019.1679134. Epub 2019 Nov 1. Nat Prod Res. 2021. PMID: 31674843
-
Phytochemical analysis and reappraisal of diuretic activity of Delphinium brunonianum Royle and its mode of action in experimental rats.Pak J Pharm Sci. 2020 Jul;33(4(Supplementary)):1833-1838. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2020. PMID: 33612467
-
Ferulic acid, a natural polyphenol, alleviates insulin resistance and hypertension in fructose fed rats: Effect on endothelial-dependent relaxation.Chem Biol Interact. 2016 Jul 25;254:191-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2016.06.013. Epub 2016 Jun 7. Chem Biol Interact. 2016. PMID: 27287418
-
The potential protective effect of the Polygonum hydropiper L against the development of fructose-induced oxidative stress and metabolic disorders in male Sprague-Dawely rats.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 20;74(4):585-595. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgab071. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34165561
-
Dioscoreophyllum cumminsii (Stapf) Diels leaves halt high-fructose induced metabolic syndrome: Hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, inflammation and oxidative stress.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Nov 4;192:471-479. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.08.024. Epub 2016 Aug 26. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27568876
Cited by
-
Thymus musilii Velen. Methanolic Extract: In Vitro and In Silico Screening of Its Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, Anti-Quorum Sensing, Antibiofilm, and Anticancer Activities.Life (Basel). 2022 Dec 25;13(1):62. doi: 10.3390/life13010062. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36676011 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ebrahimi-Mameghani M., Asghari-Jafarabadi M., Rezazadeh K. TCF7L2-rs7903146 polymorphism modulates the effect of artichoke leaf extract supplementation on insulin resistance in metabolic syndrome: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Integr. Med. 2018;16:329–334. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2018.05.006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kamboj V.P. Herbal medicine. Curr. Sci. 2000;78:35–39.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

