Safe Medication Management for Polymedicated Home-Dwelling Older Adults after Hospital Discharge: A Qualitative Study of Older Adults, Informal Caregivers and Healthcare Professionals' Perspectives
- PMID: 35736616
- PMCID: PMC9230543
- DOI: 10.3390/nursrep12020039
Safe Medication Management for Polymedicated Home-Dwelling Older Adults after Hospital Discharge: A Qualitative Study of Older Adults, Informal Caregivers and Healthcare Professionals' Perspectives
Abstract
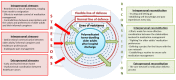
Safe medication management is particularly challenging among polymedicated home-dwelling older adults after hospital discharge. This study aimed to identify and categorise the stressors experienced and reconstitution strategies adopted by older adults, their informal caregivers, and healthcare professionals as they manage older adults' medications after hospital discharge. A primary study collected the perspectives of 28 older adults, 17 informal caregivers, and 13 healthcare professionals using a qualitative descriptive design. The Neuman Systems Model was used as the basis for a secondary deductive content analysis. Findings revealed that post-discharge medication management at home involved numerous stressors, often including dysfunctions in communication, collaboration, and coordination between the multiple stakeholders involved. Reconstitution strategies for safe medication management were not always successful or satisfactory and were sometimes identified as stressors themselves. Older adults, informal caregivers, and healthcare professionals' perspectives highlighted several potential opportunities for improving safe medication management through nurse-led, interprofessional, patient-centred practices.
Keywords: Neuman Systems Model; home-dwelling older adults; hospital discharge; informal caregivers; interprofessional collaboration; reconstitution; safe medication management; secondary deductive content analysis; stressors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in study design, the collection, analysis or interpretation of data, writing the manuscript or the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Monégat M., Sermet C. La polymédication définitions, mesures et enjeux: Revue de la littérature et tests de mesure. Quest. D’économie De La St. 2014;204:1–8.
-
- Ozkan I., Taskin Yilmaz F., Karakoc Kumsar A., Uyar K. Knowledge, Attitude and Behaviours regarding Medication Use in Elderly with Chronic Diseases in Turkey. Elder. Health J. 2020;6:42–49.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources