Changes in the Oxidative Stress Status of Dogs Affected by Acute Enteropathies
- PMID: 35737327
- PMCID: PMC9228746
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci9060276
Changes in the Oxidative Stress Status of Dogs Affected by Acute Enteropathies
Abstract
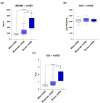
Canine acute enteropathies (AE) are common morbidities primarily managed with supportive therapy. However, in some cases, unnecessary courses of antibiotics are empirically prescribed. Recent studies in humans have hypothesized the use of antioxidants as a possible alternative and/or support to antimicrobial drugs in uncomplicated cases. Considering the global need to reduce the antibiotic use, the aim of the study was to compare the oxidative burden of the diarrhetic population to that of healthy dogs. Forty-five patients suffering from uncomplicated acute diarrhea (AD) and 30 controls were screened for clinical and biochemical parameters, and serum redox indices (reactive oxygen metabolites, dROMs; serum antioxidant capacity, SAC; oxidative stress index, OSi). The average levels of dROMs in AD dogs were significantly higher (p < 0.001) than in healthy dogs, while SAC did not significantly differ between the two groups. However, the OSi values (ratio between dROMs and SAC) significantly increased (p < 0.001) in AD dogs compared to controls. The study demonstrates that canine AD could induce redox imbalance. Although its role in the etiopathogenesis and evolution of the disease should be further investigated, our results suggest that the improvement of the patient oxidative status, possibly through the dietary administration of antioxidants, could support the management of canine AE, reducing the use of antibiotics.
Keywords: acute diarrhea; antioxidant status; dog; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Willard M.D. Clinical Manifestations of Gastrointestinal Disorders. In: Nelson R.W., Couto C.G., editors. Small Animal Internal Medicine. 6th ed. Elsevier; St. Louis, MO, USA: 2019. pp. 389–411.
-
- Werner M., Unterer S. Antibiotikaeinsatz beim akuten Durchfall des Hundes—Übersicht potenzieller Risiken, Indikationen und Alternativen [Use of antimicrobials in acute canine diarrhea—Overview of potential risks, indications and alternatives] Tierarztl. Prax. Ausg. K Kleintiere Heimtiere. 2021;49:110–120. doi: 10.1055/a-1395-2001. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

