Analysis of the Expression of Neurotrophins and Their Receptors in Adult Zebrafish Kidney
- PMID: 35737348
- PMCID: PMC9227799
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci9060296
Analysis of the Expression of Neurotrophins and Their Receptors in Adult Zebrafish Kidney
Abstract
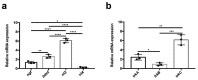
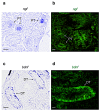
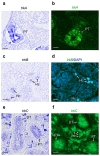
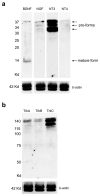
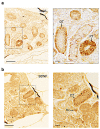
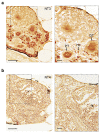
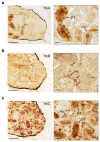
Neurotrophins and their receptors are involved in the development and maintenance of neuronal populations. Different reports have shown that all neurotrophin/receptor pathways can also play a role in several non-neuronal tissues in vertebrates, including the kidney. These signaling pathways are involved in different events to ensure the correct functioning of the kidney, such as growth, differentiation, and regulation of renal tubule transport. Previous studies in some fish species have identified the neurotrophins and receptors in the kidney. In this study, for the first time, we compare the expression profiles (mRNA and protein) of all neurotrophin/receptor pathways in the kidney of the adult zebrafish. We quantify the levels of mRNA by using qPCR and identify the expression pattern of each neurotrophin/receptor pathway by in situ hybridization. Next, we detect the proteins using Western blotting and immunohistochemistry. Our results show that among all neurotrophins analyzed, NT-3/TrkC is the most expressed in the glomerule and tubule and in the hematopoietic cells, similar to what has been reported in the mammalian kidney.
Keywords: Trk receptor; kidney; neurotrophin; zebrafish.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ibanez C.F., Hallbook F., Godeau F., Persson H. Expression of neurotrophin-4 mRNA during oogenesis in Xenopus laevis. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 1992;36:239–245. - PubMed
-
- Islam N., Gagnon F., Moss T. Catalytic and non-catalytic forms of the neurotrophin receptor xTrkB mRNA are expressed in a pseudo-segmental manner within the early Xenopus central nervous system. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 1996;40:973–983. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

