Tumor necrosis factor induces pathogenic mitochondrial ROS in tuberculosis through reverse electron transport
- PMID: 35737799
- PMCID: PMC7612974
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abh2841
Tumor necrosis factor induces pathogenic mitochondrial ROS in tuberculosis through reverse electron transport
Abstract
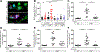
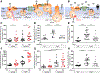
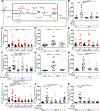
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a critical host resistance factor against tuberculosis. However, excess TNF produces susceptibility by increasing mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (mROS), which initiate a signaling cascade to cause pathogenic necrosis of mycobacterium-infected macrophages. In zebrafish, we identified the mechanism of TNF-induced mROS in tuberculosis. Excess TNF in mycobacterium-infected macrophages elevates mROS production by reverse electron transport (RET) through complex I. TNF-activated cellular glutamine uptake leads to an increased concentration of succinate, a Krebs cycle intermediate. Oxidation of this elevated succinate by complex II drives RET, thereby generating the mROS superoxide at complex I. The complex I inhibitor metformin, a widely used antidiabetic drug, prevents TNF-induced mROS and necrosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected zebrafish and human macrophages; metformin may therefore be useful in tuberculosis therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
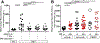
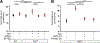
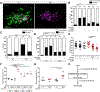
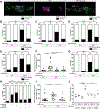
References
-
- Keane J et al., Tuberculosis associated with infliximab, a tumor necrosis factor alpha-neutralizing agent. N Engl J Med 345, 1098–1104 (2001). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

