Electrochemical biosensors for SARS-CoV-2 detection: Voltametric or impedimetric transduction?
- PMID: 35738049
- PMCID: PMC9188450
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2022.108190
Electrochemical biosensors for SARS-CoV-2 detection: Voltametric or impedimetric transduction?
Abstract
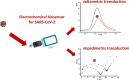
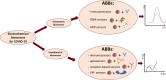
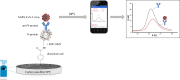
During the COVID-19 pandemic, electrochemical biosensors have shown several advantages including accuracy, low cost, possibility of miniaturization and portability, which make them an interesting testing method for rapid point-of-care (POC) detection of SARS-CoV-2 infection, allowing the detection of both viral RNA and viral antigens. Herein, we reviewed advancements in electrochemical biosensing platforms towards the detection of SARS-CoV-2 based on voltametric and impedimetric transduction modes, highlighting the advantages and drawbacks of the two methods.
Keywords: Aptasensor; DNA-sensor; Immunosensor; Impedimetric biosensor; MIP-sensor; SARS-CoV-2; Voltametric biosensor.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The potential application of electrochemical biosensors in the COVID-19 pandemic: A perspective on the rapid diagnostics of SARS-CoV-2.Biosens Bioelectron. 2021 Mar 15;176:112905. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112905. Epub 2020 Dec 17. Biosens Bioelectron. 2021. PMID: 33358285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Voltammetric-based immunosensor for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid antigen.Mikrochim Acta. 2021 May 26;188(6):199. doi: 10.1007/s00604-021-04867-1. Mikrochim Acta. 2021. PMID: 34041585 Free PMC article.
-
Utilizing Electrochemical-Based Sensing Approaches for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Clinical Samples: A Review.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Jun 29;12(7):473. doi: 10.3390/bios12070473. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Developments in Electrochemical-Impedimetric Biosensors for Virus Detection.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 14;23(24):15922. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415922. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2-Impedimetric Biosensor: Virus-Imprinted Chips for Early and Rapid Diagnosis.ACS Sens. 2021 Nov 26;6(11):4098-4107. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.1c01614. Epub 2021 Nov 10. ACS Sens. 2021. PMID: 34757734
Cited by
-
Carbon-based nanomaterials against SARS-CoV-2: Therapeutic and diagnostic applications.OpenNano. 2023 Mar;10:100121. doi: 10.1016/j.onano.2023.100121. Epub 2023 Feb 18. OpenNano. 2023. PMID: 40478147 Free PMC article.
-
Electronic Tongue for Direct Assessment of SARS-CoV-2-Free and Infected Human Saliva-A Feasibility Study.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Jul 7;13(7):717. doi: 10.3390/bios13070717. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37504115 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Virus via Fiber-Optic and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Based Aptasensors.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 May 7;14(5):231. doi: 10.3390/bios14050231. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38785705 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Progress in PDMS-Based Microfluidics Toward Integrated Organ-on-a-Chip Biosensors and Personalized Medicine.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 Jan 29;15(2):76. doi: 10.3390/bios15020076. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39996978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Organic Electrochemical Transistor Immuno-Sensors for Spike Protein Early Detection.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Jul 17;13(7):739. doi: 10.3390/bios13070739. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37504137 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO, COVID-19 Weekly Epidemiological Update 35, World Heal. Organ., 2021, pp. 1–3, https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation reports/weekly_epidemiological_update_22.pdf.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

