Changes in laboratory value improvement and mortality rates over the course of the pandemic: an international retrospective cohort study of hospitalised patients infected with SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 35738646
- PMCID: PMC9226470
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-057725
Changes in laboratory value improvement and mortality rates over the course of the pandemic: an international retrospective cohort study of hospitalised patients infected with SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
Objective: To assess changes in international mortality rates and laboratory recovery rates during hospitalisation for patients hospitalised with SARS-CoV-2 between the first wave (1 March to 30 June 2020) and the second wave (1 July 2020 to 31 January 2021) of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Design, setting and participants: This is a retrospective cohort study of 83 178 hospitalised patients admitted between 7 days before or 14 days after PCR-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection within the Consortium for Clinical Characterization of COVID-19 by Electronic Health Record, an international multihealthcare system collaborative of 288 hospitals in the USA and Europe. The laboratory recovery rates and mortality rates over time were compared between the two waves of the pandemic.
Primary and secondary outcome measures: The primary outcome was all-cause mortality rate within 28 days after hospitalisation stratified by predicted low, medium and high mortality risk at baseline. The secondary outcome was the average rate of change in laboratory values during the first week of hospitalisation.
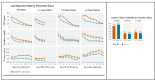
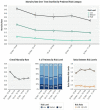
Results: Baseline Charlson Comorbidity Index and laboratory values at admission were not significantly different between the first and second waves. The improvement in laboratory values over time was faster in the second wave compared with the first. The average C reactive protein rate of change was -4.72 mg/dL vs -4.14 mg/dL per day (p=0.05). The mortality rates within each risk category significantly decreased over time, with the most substantial decrease in the high-risk group (42.3% in March-April 2020 vs 30.8% in November 2020 to January 2021, p<0.001) and a moderate decrease in the intermediate-risk group (21.5% in March-April 2020 vs 14.3% in November 2020 to January 2021, p<0.001).
Conclusions: Admission profiles of patients hospitalised with SARS-CoV-2 infection did not differ greatly between the first and second waves of the pandemic, but there were notable differences in laboratory improvement rates during hospitalisation. Mortality risks among patients with similar risk profiles decreased over the course of the pandemic. The improvement in laboratory values and mortality risk was consistent across multiple countries.
Keywords: COVID-19; Epidemiology; Public health.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000005/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001878/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS098023/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS124882/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL151643/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD040128/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001420/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES017885/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 LM012095/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008685/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001998/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002366/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001857/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- T15 LM007092/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG009174/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA210967/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 LM013345/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002541/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 LM013337/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL148394/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002240/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- L40 HL148910/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
