Retinal vascular occlusion in patients with the Covid-19 virus
- PMID: 35739568
- PMCID: PMC9219213
- DOI: 10.1186/s40942-022-00371-7
Retinal vascular occlusion in patients with the Covid-19 virus
Abstract
Background: The coronavirus disease (COVID-19) can cause acute respiratory distress syndrome with dyspnea, anosmia, fever, and cough. Few studies describing ocular findings have been reported. The current case series, reports the clinical findings and natural history of patients with retinal vascular occlusion after COVID-19 infection.
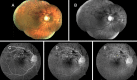
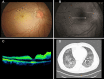
Case presentations: Patients from multiple Brazilian hospitals who had clinical and laboratory diagnoses of COVID-19 with retinal vein or arterial occlusion were analyzed retrospectively. The baseline demographics, clinical presentations of COVID-19, comorbidities, risk factors for thromboembolic events, and use of anticoagulant drugs were reviewed. The relevant clinical findings associated with the retinal vascular occlusive event, management, and outcomes were reported. Fourteen cases of retinal vascular occlusion within 3 months of the laboratory confirmed COVID-19 infection were identified. Three of which required hospitalization for COVID-19 management. Eight cases had central retinal vein occlusion, three branch retinal vein occlusion, one hemispheric retinal vein occlusion, and two central arterial occlusion. The mean patient age at presentation was 48 years; the visual acuity ranged from light perception to 20/20. Nine patients received intravitreal injections of anti-angiogenic drugs and one received ketorolac tromethamine drops for the management of secondary macular edema; four were untreated.
Conclusions: COVID-19 patients may rarely have ocular manifestations of the disease. It was presented a case series of vascular occlusion events that may be related to COVID-19 infection, since these thrombotic events are actively involved in the disease pathophysiology. These cases emphasize the need for further investigation of ocular complications associated with this disease.
Keywords: COVID-19; Intravitreal injections; Retina; Thromboembolic phenomena; Vascular occlusion.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
None of authors have any proprietary interests or conflicts of interest related to this submission.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

