Alanyl-Glutamine Protects against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Liver Injury in Mice via Alleviating Oxidative Stress, Inhibiting Inflammation, and Regulating Autophagy
- PMID: 35739966
- PMCID: PMC9220087
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11061070
Alanyl-Glutamine Protects against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Liver Injury in Mice via Alleviating Oxidative Stress, Inhibiting Inflammation, and Regulating Autophagy
Abstract
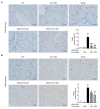
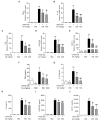
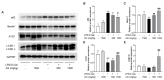
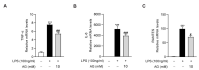
Acute liver injury is a worldwide problem with a high rate of morbidity and mortality, and effective pharmacological therapies are still urgently needed. Alanyl-glutamine (Ala-Gln), a dipeptide formed from L-alanine and L-glutamine, is known as a protective compound that is involved in various tissue injuries, but there are limited reports regarding the effects of Ala-Gln in acute liver injury. This present study aimed to investigate the protective effects of Ala-Gln in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute liver injury in mice, with a focus on inflammatory responses and oxidative stress. The acute liver injury induced using LPS (50 μg/kg) and D-galactosamine (D-Gal) (400 mg/kg) stimulation in mice was significantly attenuated after Ala-Gln treatment (500 and 1500 mg/kg), as evidenced by reduced plasma alanine transaminase (ALT) (p < 0.01, p < 0.001), aspartate transaminase (AST) (p < 0.05, p < 0.001), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) (p < 0.01, p < 0.001) levels, and accompanied by improved histopathological changes. In addition, LPS/D-Gal-induced hepatic apoptosis was also alleviated by Ala-Gln administration, as shown by a greatly decreased ratio of TUNEL-positive hepatocytes, from approximately 10% to 2%, and markedly reduced protein levels of cleaved caspase-3 (p < 0.05, p < 0.001) in liver. Moreover, we found that LPS/D-Gal-triggered oxidative stress was suppressed after Ala-Gln treatment, the effect of which might be dependent on the elevation of SOD and GPX activities, and on GSH levels in liver. Interestingly, we observed that Ala-Gln clearly inhibited LPS/D-Gal exposure-induced macrophage accumulation and the production of proinflammatory factors in the liver. Furthermore, Ala-Gln greatly regulated autophagy in the liver in LPS/D-Gal-treated mice. Using RAW264.7 cells, we confirmed the anti-inflammatory role of Ala-Gln-targeting macrophages.
Keywords: acute liver injury; alanyl-glutamine; apoptosis; inflammation; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

