Antioxidants in Arrhythmia Treatment-Still a Controversy? A Review of Selected Clinical and Laboratory Research
- PMID: 35740006
- PMCID: PMC9220256
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11061109
Antioxidants in Arrhythmia Treatment-Still a Controversy? A Review of Selected Clinical and Laboratory Research
Abstract
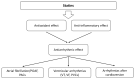
Antioxidants are substances that can prevent damage to cells caused by free radicals. Production of reactive oxygen species and the presence of oxidative stress play an important role in cardiac arrhythmias. Currently used antiarrhythmic drugs have many side effects. The research on animals and humans using antioxidants (such as vitamins C and E, resveratrol and synthetic substances) yields many interesting but inconclusive results. Natural antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, can reduce the recurrence of atrial fibrillation (AF) after successful electrical cardioversion and protect against AF after cardiac surgery, but do not affect the incidence of atrial arrhythmias in critically ill patients with trauma. Vitamins C and E may also effectively treat ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation and long QT-related arrhythmias. Another natural antioxidant-resveratrol-may effectively treat AF and ventricular arrhythmias caused by ischaemia-reperfusion injury. It reduces the mortality associated with life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias and can be used to prevent myocardial remodelling. Statins also show antioxidant activity. Their action is related to the reduction of oxidative stress and anti-inflammatory effect. Therefore, statins can reduce the post-operative risk of AF and may be useful in lowering its recurrence rate after successful cardioversion. Promising results also apply to polyphenols, nitric oxide synthase inhibitors and MitoTEMPO. Although few clinical trials have been conducted, the use of antioxidants in treating arrhythmias is an interesting prospect.
Keywords: antioxidants; atrial fibrillation; resveratrol; ventricular arrhythmia; vitamin C; vitamin E.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Advanced electrophysiologic mapping systems: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006;6(8):1-101. Epub 2006 Mar 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006. PMID: 23074499 Free PMC article.
-
Tracing the origins of postoperative atrial fibrillation: the concept of oxidative stress-mediated myocardial injury phenomenon.Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2008 Dec;15(6):735-41. doi: 10.1097/HJR.0b013e328317f38a. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2008. PMID: 19020458 Review.
-
Antioxidants for prevention of atrial fibrillation: a potentially useful future therapeutic approach? A review of the literature and meta-analysis.Europace. 2014 Aug;16(8):1107-16. doi: 10.1093/europace/euu040. Epub 2014 Apr 4. Europace. 2014. PMID: 24706090 Review.
-
Silymarin and vitamin E do not attenuate and vitamin E might even enhance the antiarrhythmic activity of amiodarone in a rat reperfusion arrhythmia model.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2001;15(3):233-40. doi: 10.1023/a:1011916306782. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2001. PMID: 11713891
-
Pharmacological approaches in the treatment of atrial fibrillation.Curr Med Chem. 2004 Jan;11(1):13-28. doi: 10.2174/0929867043456241. Curr Med Chem. 2004. PMID: 14754423 Review.
Cited by
-
IL-11 promotes Ang II-induced autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial dysfunction in atrial fibroblasts.Open Life Sci. 2025 Mar 11;20(1):20251063. doi: 10.1515/biol-2025-1063. eCollection 2025. Open Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40092733 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative and postoperative administration of vitamin C in cardiac surgery patients - settings, dosages, duration, and clinical outcomes: a narrative review.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024 Apr 29;86(6):3591-3607. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000002112. eCollection 2024 Jun. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38846824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural polyphenols as novel interventions for aging and age-related diseases: Exploring efficacy, mechanisms of action and implications for future research.Chin Herb Med. 2024 Sep 3;17(2):279-291. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2024.09.001. eCollection 2025 Apr. Chin Herb Med. 2024. PMID: 40256718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selenium as a Modulator of Redox Reactions in the Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jun 3;13(6):688. doi: 10.3390/antiox13060688. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Redox imbalance in patients with heart failure and ICD/CRT-D intervention. Can it be an underappreciated and overlooked arrhythmogenic factor? A first preliminary clinical study.Front Physiol. 2023 Nov 8;14:1289587. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1289587. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 38028798 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

