Nrf2 Activation in Chronic Kidney Disease: Promises and Pitfalls
- PMID: 35740009
- PMCID: PMC9220138
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11061112
Nrf2 Activation in Chronic Kidney Disease: Promises and Pitfalls
Abstract
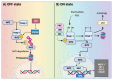
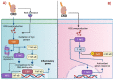
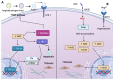
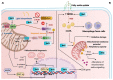
The nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) protects the cell against oxidative damage. The Nrf2 system comprises a complex network that functions to ensure adequate responses to redox perturbations, but also metabolic demands and cellular stresses. It must be kept within a physiologic activity range. Oxidative stress and alterations in Nrf2-system activity are central for chronic-kidney-disease (CKD) progression and CKD-related morbidity. Activation of the Nrf2 system in CKD is in multiple ways related to inflammation, kidney fibrosis, and mitochondrial and metabolic effects. In human CKD, both endogenous Nrf2 activation and repression exist. The state of the Nrf2 system varies with the cause of kidney disease, comorbidities, stage of CKD, and severity of uremic toxin accumulation and inflammation. An earlier CKD stage, rapid progression of kidney disease, and inflammatory processes are associated with more robust Nrf2-system activation. Advanced CKD is associated with stronger Nrf2-system repression. Nrf2 activation is related to oxidative stress and moderate uremic toxin and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) elevations. Nrf2 repression relates to high uremic toxin and NF-κB concentrations, and may be related to Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1)-independent Nrf2 degradation. Furthermore, we review the effects of pharmacological Nrf2 activation by bardoxolone methyl, curcumin, and resveratrol in human CKD and outline strategies for how to adapt future Nrf2-targeted therapies to the requirements of patients with CKD.
Keywords: CKD; NQO1; Nrf2; bardoxolone methyl; curcumin; fibrosis; hemodialysis; inflammation; kidney function; oxidative stress; redox signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group KDIGO 2012 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Inter. 2013;3:1–150.
-
- Bikbov B., Purcell C.A., Levey A.S., Smith M., Abdoli A., Abebe M., Adebayo O.M., Afarideh M., Agarwal S.K., Agudelo-Botero M., et al. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet. 2020;395:709–733. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30045-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

