Molecular Mechanisms behind Safranal's Toxicity to HepG2 Cells from Dual Omics
- PMID: 35740022
- PMCID: PMC9219844
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11061125
Molecular Mechanisms behind Safranal's Toxicity to HepG2 Cells from Dual Omics
Abstract
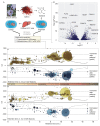
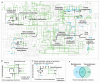
The spice saffron (Crocus sativus) has anticancer activity in several human tissues, but the molecular mechanisms underlying its potential therapeutic effects are poorly understood. We investigated the impact of safranal, a small molecule secondary metabolite from saffron, on the HCC cell line HepG2 using untargeted metabolomics (HPLC-MS) and transcriptomics (RNAseq). Increases in glutathione disulfide and other biomarkers for oxidative damage contrasted with lower levels of the antioxidants biliverdin IX (139-fold decrease, p = 5.3 × 105), the ubiquinol precursor 3-4-dihydroxy-5-all-trans-decaprenylbenzoate (3-fold decrease, p = 1.9 × 10-5), and resolvin E1 (-3282-fold decrease, p = 45), which indicates sensitization to reactive oxygen species. We observed a significant increase in intracellular hypoxanthine (538-fold increase, p = 7.7 × 10-6) that may be primarily responsible for oxidative damage in HCC after safranal treatment. The accumulation of free fatty acids and other biomarkers, such as S-methyl-5'-thioadenosine, are consistent with safranal-induced mitochondrial de-uncoupling and explains the sharp increase in hypoxanthine we observed. Overall, the dual omics datasets describe routes to widespread protein destabilization and DNA damage from safranal-induced oxidative stress in HCC cells.
Keywords: DNA damage; cancer; hepatocellular carcinoma; hypoxanthine; natural products; saffron; safranal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

