The Protective Anticancer Effect of Natural Lycopene Supercritical CO2 Watermelon Extracts in Adenocarcinoma Lung Cancer Cells
- PMID: 35740047
- PMCID: PMC9219748
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11061150
The Protective Anticancer Effect of Natural Lycopene Supercritical CO2 Watermelon Extracts in Adenocarcinoma Lung Cancer Cells
Abstract
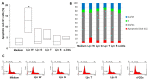
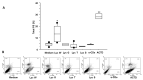
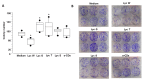
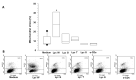
Carotenoids may have different effects on cancer and its progression. The safety of carotenoid supplements was evaluated in vitro on human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) adenocarcinoma A549 cells by the administration of three different oleoresins containing lycopene and other lipophilic phytochemicals, such as tocochromanols. The oleoresins, obtained by the supercritical CO2 green extraction technology from watermelon (Lyc W), gấc(Lyc G) and tomato (Lyc T) and chlatrated in α-cyclodextrins, were tested in comparison to synthetic lycopene (Lyc S), by cell cycle, Annexin V-FITC/PI, clonogenic test, Mytosox, intracellular ROS, Western Blot for NF-kB and RT-PCR and ELISA for IL-8. The extracts administered at the same lycopene concentration (10 µM) showed conflicting behaviors: Lyc W, with the highest lycopene/tocochromanols ratio, significantly increased cell apoptosis, mitochondrial stress, intracellular ROS, NF-kB and IL-8 expression and significantly decreased cell proliferation, whereas Lyc G and Lyc T significantly increased only cell proliferation. Lyc S treatment was ineffective. The highest amount of lycopene in Lyc W was able to counteract and revert the cell survival effect of tocochromanols supporting the importance of evaluating the lycopene bio-availability and the real effect of antioxidant tocochromanols' supplementation which may not only have no anticancer benefits but may even increase cancer aggressivity.
Keywords: antioxidants; carotenoids; inflammation; lung cancer; lycopene; lycopene from gấc; lycopene from tomato; lycopene from watermelon; supercritical fluid extraction; synthetic lycopene; tocochromanols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Supercritical CO2 extraction of tomato pomace: Evaluation of the solubility of lycopene in tomato oil as limiting factor of the process performance.Food Chem. 2020 Jun 15;315:126224. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126224. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Food Chem. 2020. PMID: 32007813
-
Supplementation with tomato-based products increases lycopene, phytofluene, and phytoene levels in human serum and protects against UV-light-induced erythema.Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2005 Jan;75(1):54-60. doi: 10.1024/0300-9831.75.1.54. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2005. PMID: 15830922 Clinical Trial.
-
Lycopene ameliorates chronic stress-induced hippocampal injury and subsequent learning and memory dysfunction through inhibiting ROS/JNK signaling pathway in rats.Food Chem Toxicol. 2020 Nov;145:111688. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2020.111688. Epub 2020 Aug 15. Food Chem Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32810585
-
Lycopene - antioxidant with radioprotective and anticancer properties. A review.Rocz Panstw Zakl Hig. 2014;65(4):263-71. Rocz Panstw Zakl Hig. 2014. PMID: 25526570 Review.
-
An Overview of Properties and Analytical Methods for Lycopene in Organic Nanocarriers.Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2021;51(7):674-686. doi: 10.1080/10408347.2020.1763774. Epub 2020 May 15. Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2021. PMID: 32412352 Review.
Cited by
-
Relationship among Body Composition, Adipocytokines, and Irisin on Exercise Capacity and Quality of Life in COPD: A Pilot Study.Biomolecules. 2022 Dec 27;13(1):48. doi: 10.3390/biom13010048. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36671433 Free PMC article.
-
Natural products targeting inflammation-related metabolic disorders: A comprehensive review.Heliyon. 2023 Jun 2;9(6):e16919. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16919. eCollection 2023 Jun. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37346355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Citrullus mucosospermus Extract Exerts Protective Effects against Methionine- and Choline-Deficient Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Mice.Foods. 2024 Jul 1;13(13):2101. doi: 10.3390/foods13132101. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38998607 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Insights into the Role of the Antioxidants in Prostate Pathology.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jan 27;12(2):289. doi: 10.3390/antiox12020289. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physicochemical properties, mechanism of action of lycopene and its application in poultry and ruminant production.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Mar 18;11:1364589. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1364589. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38562916 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Meléndez-Martínez A.J., Böhm V., Borge G.I.A., Cano M.P., Fikselová M., Gruskiene R., Lavelli V., Loizzo M.R., Mandić A.I., Brahm P.M., et al. Carotenoids: Considerations for Their Use in Functional Foods, Nutraceuticals, Nutricosmetics, Supplements, Botanicals, and Novel Foods in the Context of Sustainability, Circular Economy, and Climate Change. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2021;12:433–460. doi: 10.1146/annurev-food-062220-013218. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cvetkovic D., Fiedor L., Fiedor J., Wiśniewska-Becker A., Markovic D. Carotenoids: Food Sources, Production and Health Benefits. Nova Science Publishers, Inc.; Hauppauge, NY, USA: 2013. Molecular Base for Carotenoids Antioxidant Activity in Model and Biological Systems: The Health-Related Effects; pp. 93–126.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

