The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in the Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Synovial Microenvironment
- PMID: 35740050
- PMCID: PMC9220354
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11061153
The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in the Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Synovial Microenvironment
Abstract
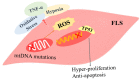
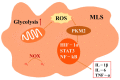
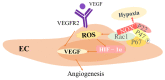
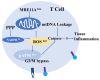
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an inflammatory disease that begins with a loss of tolerance to modified self-antigens and immune system abnormalities, eventually leading to synovitis and bone and cartilage degradation. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are commonly used as destructive or modifying agents of cellular components or they act as signaling molecules in the immune system. During the development of RA, a hypoxic and inflammatory situation in the synovium maintains ROS generation, which can be sustained by increased DNA damage and malfunctioning mitochondria in a feedback loop. Oxidative stress caused by abundant ROS production has also been shown to be associated with synovitis in RA. The goal of this review is to examine the functions of ROS and related molecular mechanisms in diverse cells in the synovial microenvironment of RA. The strategies relying on regulating ROS to treat RA are also reviewed.
Keywords: reactive oxygen species; rheumatoid arthritis; synovium; synovium microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Arnett F.C., Edworthy S.M., Bloch D.A., McShane D.J., Fries J.F., Cooper N.S., Healey L.A., Kaplan S.R., Liang M.H., Luthra H.S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988;31:315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

