Oxidative Stress Parameters as Biomarkers of Cardiovascular Disease towards the Development and Progression
- PMID: 35740071
- PMCID: PMC9219727
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11061175
Oxidative Stress Parameters as Biomarkers of Cardiovascular Disease towards the Development and Progression
Abstract
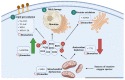
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) remains the leading cause of death globally, with unhealthy lifestyles today greatly increasing the risk. Over the decades, scientific investigation has been carried out on reactive oxygen species (ROS) and their resultant oxidative stress based on their changes made on biological targets such as lipids, proteins, and DNA. Since the existing clinical studies with antioxidants failed to provide relevant findings on CVD prediction, the focus has shifted towards recognition of oxidised targets as biomarkers to predict prognosis and response to accurate treatment. The identification of redox markers could help clinicians in providing risk stratification for CVD events beyond the traditional prognostic and diagnostic targets. This review will focus on how oxidant-related parameters can be applied as biomarkers for CVD based on recent clinical evidence.
Keywords: biomarkers; cardiovascular; oxidant; oxidative stress; reactive oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Noncommunicable Diseases. [(accessed on 13 April 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/noncommunicable-diseases.
-
- Dai H., Much A.A., Maor E., Asher E., Younis A., Xu Y., Lu Y., Liu X., Shu J., Bragazzi N.L. Global, regional, and national burden of ischaemic heart disease and its attributable risk factors, 1990–2017: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Eur. Heart J. Qual. Care Clin. Outcomes. 2020;8:50–60. doi: 10.1093/ehjqcco/qcaa076. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

