Exogenous Melatonin in the Culture Medium Does Not Affect the Development of In Vivo-Derived Pig Embryos but Substantially Improves the Quality of In Vitro-Produced Embryos
- PMID: 35740074
- PMCID: PMC9220299
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11061177
Exogenous Melatonin in the Culture Medium Does Not Affect the Development of In Vivo-Derived Pig Embryos but Substantially Improves the Quality of In Vitro-Produced Embryos
Abstract
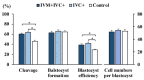
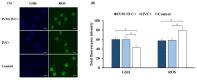
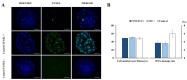
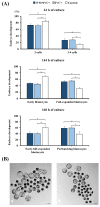
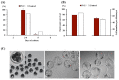
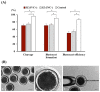
Cloned and transgenic pigs are relevant human disease models and serve as potential donors for regenerative medicine and xenotransplantation. These technologies demand oocytes and embryos of good quality. However, the current protocols for in vitro production (IVP) of pig embryos give reduced blastocyst efficiency and embryo quality compared to in vivo controls. This is likely due to culture conditions jeopardizing embryonic homeostasis including the effect of reactive oxygen species (ROS) influence. In this study, the antioxidant melatonin (1 nM) in the maturation medium, fertilization medium, or both media was ineffective in enhancing fertilization or embryonic development parameters of in vitro fertilized oocytes. Supplementation of melatonin in the fertilization medium also had no effect on sperm function. In contrast, the addition of melatonin to the embryo culture medium accelerated the timing of embryonic development and increased the percentages of cleaved embryos and presumed zygotes that developed to the blastocyst stage. Furthermore, it increased the number of inner mass cells and the inner mass cell/total cell number ratio per blastocyst while increasing intracellular glutathione and reducing ROS and DNA damage levels in embryos. Contrarily, the addition of melatonin to the embryo culture medium had no evident effect on in vivo-derived embryos, including the developmental capacity and the quality of in vivo-derived 4-cell embryos or the percentage of genome-edited in vivo-derived zygotes achieving the blastocyst stage. In conclusion, exogenous melatonin in the embryo culture medium enhances the development and quality of in vitro-derived embryos but not in in vivo-derived embryos. Exogenous melatonin is thus recommended during embryo culture of oocytes matured and fertilized in vitro for improving porcine IVP efficiency.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; apoptosis; in vitro fertilization; in vivo-derived embryos; inner cell mass; melatonin; pig; reactive oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

