Effect of Low-Dose Radiotherapy on the Circulating Levels of Paraoxonase-1-Related Variables and Markers of Inflammation in Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia
- PMID: 35740079
- PMCID: PMC9220239
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11061184
Effect of Low-Dose Radiotherapy on the Circulating Levels of Paraoxonase-1-Related Variables and Markers of Inflammation in Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia
Abstract
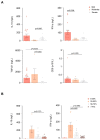
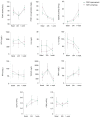
The aim of our study was to investigate the changes produced by low-dose radiotherapy (LDRT) in the circulating levels of the antioxidant enzyme paraoxonase-1 (PON1) and inflammatory markers in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia treated with LDRT and their interactions with clinical and radiological changes. Data were collected from the IPACOVID prospective clinical trial (NCT04380818). The study included 30 patients treated with a whole-lung dose of 0.5 Gy. Clinical follow-up, as well as PON1-related variables, cytokines, and radiological parameters were analyzed before LDRT, at 24 h, and 1 week after treatment. Twenty-five patients (83.3%) survived 1 week after LDRT. Respiratory function and radiological images improved in survivors. Twenty-four hours after LDRT, PON1 concentration significantly decreased, while transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1) increased with respect to baseline. One week after LDRT, patients had increased PON1 activities and lower PON1 and TGF-β1 concentrations compared with 24 h after LDRT, PON1 specific activity increased, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and C-reactive protein (CRP) decreased, and CD4+ and CD8+ cells increased after one week. Our results highlight the benefit of LDRT in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and it might be mediated, at least in part, by an increase in serum PON1 activity at one week and an increase in TGF-β1 concentrations at 24 h.
Keywords: COVID-19 pneumonia; chemokines; low-dose radiation therapy; paraoxonase-1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Camps J., Castañé H., Rodríguez-Tomàs E., Baiges-Gaya G., Hernández-Aguilera A., Arenas M., Iftimie S., Joven J. On the role of paraoxonase-1 and chemokine ligand 2 (C-C motif) in metabolic alterations linked to inflammation and disease. A 2021 update. Biomolecules. 2021;11:971. doi: 10.3390/biom11070971. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rodríguez-Tomàs E., Iftimie S., Castañé H., Baiges-Gaya G., Hernández-Aguilera A., González-Viñas M., Castro A., Camps J., Joven J. Clinical performance of paraoxonase-1-related variables and novel markers of inflammation in coronavirus disease-19. A machine learning approach. Antioxidants. 2021;10:991. doi: 10.3390/antiox10060991. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

