EpisomiR, a New Family of miRNAs, and Its Possible Roles in Human Diseases
- PMID: 35740302
- PMCID: PMC9220071
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10061280
EpisomiR, a New Family of miRNAs, and Its Possible Roles in Human Diseases
Abstract
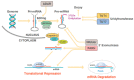
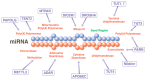
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are synthesized through a canonical pathway and play a role in human diseases, such as cancers and cardiovascular, neurodegenerative, psychiatric, and chronic inflammatory diseases. The development of sequencing technologies has enabled the identification of variations in noncoding miRNAs. These miRNA variants, called isomiRs, are generated through a non-canonical pathway, by several enzymes that alter the length and sequence of miRNAs. The isomiR family is, now, expanding further to include episomiRs, which are miRNAs with different modifications. Since recent findings have shown that isomiRs reflect the cell-specific biological function of miRNAs, knowledge about episomiRs and isomiRs can, possibly, contribute to the optimization of diagnosis and therapeutic technology for precision medicine.
Keywords: RNA modification; methylation; miRNA variants.
Conflict of interest statement
Partial institutional endowments were received from Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan), Hirotsu Bio Science Inc. (Tokyo, Japan), Kinshu-kai Medical Corporation (Osaka, Japan), Kyowa-kai Medical Corporation (Osaka, Japan), IDEA Consultants Inc. (Tokyo, Japan), and Unitech Co. Ltd. (Chiba, Japan). K.O. is an employee of IDEA Consultants Inc. (Tokyo, Japan). H.I. is a guest editor of this journal.
Figures


References
-
- Morin R.D., O’Connor M.D., Griffith M., Kuchenbauer F., Delaney A., Prabhu A.-L., Zhao Y., McDonald H., Zeng T., Hirst M., et al. Application of massively parallel sequencing to microRNA profiling and discovery in human embryonic stem cells. Genome Res. 2008;18:610–621. doi: 10.1101/gr.7179508. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

