ROCK and PDE-5 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Dementia: Literature Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35740369
- PMCID: PMC9219677
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10061348
ROCK and PDE-5 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Dementia: Literature Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
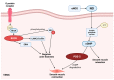
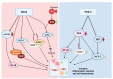
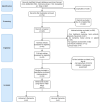
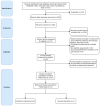
Dementia is a disease in which memory, thought, and behavior-related disorders progress gradually due to brain damage caused by injury or disease. It is mainly caused by Alzheimer's disease or vascular dementia and several other risk factors, including genetic factors. It is difficult to treat as its incidence continues to increase worldwide. Many studies have been performed concerning the treatment of this condition. Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) and phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE-5) are attracting attention as pharmacological treatments to improve the symptoms. This review discusses how ROCK and PDE-5 affect Alzheimer's disease, vascular restructuring, and exacerbation of neuroinflammation, and how their inhibition helps improve cognitive function. In addition, the results of the animal behavior analysis experiments utilizing the Morris water maze were compared through meta-analysis to analyze the effects of ROCK inhibitors and PDE-5 inhibitors on cognitive function. According to the selection criteria, 997 publications on ROCK and 1772 publications on PDE-5 were screened, and conclusions were drawn through meta-analysis. Both inhibitors showed good improvement in cognitive function tests, and what is expected of the synergy effect of the two drugs was confirmed in this review.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; ERM; LIMK; MLC; Morris water maze; PDE-5 inhibitor; ROCK inhibitor; cGMP; meta-analysis; vascular dementia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The efficacy and underlying mechanism of phosphodiesterase- 5 inhibitors in preventing cognitive impairment and Alzheimer pathology: A systematic review of animal studies.Behav Brain Res. 2019 Oct 17;372:112004. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2019.112004. Epub 2019 Jun 1. Behav Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 31163203
-
Diabetes augments cognitive dysfunction in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion by increasing neuronal cell death: implication of cilostazol for diabetes mellitus-induced dementia.Neurobiol Dis. 2015 Jan;73:12-23. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2014.08.034. Epub 2014 Oct 2. Neurobiol Dis. 2015. PMID: 25281785
-
PDE and cognitive processing: beyond the memory domain.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2015 Mar;119:108-22. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2014.10.011. Epub 2014 Nov 13. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2015. PMID: 25464010 Review.
-
Protective effects of the ROCK inhibitor fasudil against cognitive dysfunction following status epilepticus in male rats.J Neurosci Res. 2019 Apr;97(4):506-519. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24355. Epub 2018 Nov 12. J Neurosci Res. 2019. PMID: 30421453
-
PDE3 Inhibitors Repurposed as Treatments for Age-Related Cognitive Impairment.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Jun;56(6):4306-4316. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1374-4. Epub 2018 Oct 11. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30311144 Review.
Cited by
-
ROCK Inhibitor Fasudil Attenuates Neuroinflammation and Associated Metabolic Dysregulation in the Tau Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2024;21(3):183-200. doi: 10.2174/0115672050317608240531130204. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2024. PMID: 38910422 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotection by Drugs, Nutraceuticals and Physical Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 6;24(4):3176. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043176. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834601 Free PMC article.
-
Risk of dementia or cognitive impairment in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Sep 20;14:985109. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.985109. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36204558 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer's disease and neuroinflammation: will new drugs in clinical trials pave the way to a multi-target therapy?Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jun 2;14:1196413. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1196413. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37332353 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tackenberg C., Kulic L., Nitsch R.M. Familial Alzheimer′s disease mutations at position 22 of the amyloid beta-peptide sequence differentially affect synaptic loss, tau phosphorylation and neuronal cell death in an ex vivo system. PLoS ONE. 2020;15:e0239584. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0239584. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

