Human Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Produced by Different Cells: Classification of the SERS Spectra with Linear Discriminant Analysis
- PMID: 35740411
- PMCID: PMC9219671
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10061389
Human Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Produced by Different Cells: Classification of the SERS Spectra with Linear Discriminant Analysis
Abstract
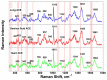
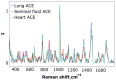
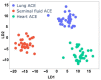
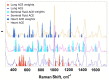
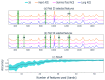
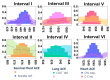
Angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) is a peptidase widely presented in human tissues and biological fluids. ACE is a glycoprotein containing 17 potential N-glycosylation sites which can be glycosylated in different ways due to post-translational modification of the protein in different cells. For the first time, surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) spectra of human ACE from lungs, mainly produced by endothelial cells, ACE from heart, produced by endothelial heart cells and miofibroblasts, and ACE from seminal fluid, produced by epithelial cells, have been compared with full assignment. The ability to separate ACEs' SERS spectra was demonstrated using the linear discriminant analysis (LDA) method with high accuracy. The intervals in the spectra with maximum contributions of the spectral features were determined and their contribution to the spectrum of each separate ACE was evaluated. Near 25 spectral features forming three intervals were enough for successful separation of the spectra of different ACEs. However, more spectral information could be obtained from analysis of 50 spectral features. Band assignment showed that several features did not correlate with band assignments to amino acids or peptides, which indicated the carbohydrate contribution to the final spectra. Analysis of SERS spectra could be beneficial for the detection of tissue-specific ACEs.
Keywords: SERS; angiotensin I-converting enzyme; full spectra assignment; glycosylation; linear discriminant analysis; nanostructured surface; tissue-specificity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tissue Specificity of Human Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 23;10(11):e0143455. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143455. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26600189 Free PMC article.
-
Knee osteoarthritis grading by resonant Raman and surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) analysis of synovial fluid.Nanomedicine. 2019 Aug;20:102012. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2019.04.015. Epub 2019 May 11. Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31085345
-
Label free hepatitis B detection based on serum derivative surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy combined with multivariate analysis.Biomed Opt Express. 2018 Sep 12;9(10):4755-4766. doi: 10.1364/BOE.9.004755. eCollection 2018 Oct 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2018. PMID: 30319900 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin converting enzyme: implications from molecular biology for its physiological functions.Int J Biochem. 1991;23(7-8):641-7. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(91)90032-i. Int J Biochem. 1991. PMID: 1650717 Review.
-
New aspects on angiotensin-converting enzyme: from gene to disease.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2002 Mar;40(3):256-65. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2002.042. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2002. PMID: 12005216 Review.
Cited by
-
Selective Detection of Fungal and Bacterial Glycans with Galactofuranose (Galf) Residues by Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering and Machine Learning Methods.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 29;26(9):4218. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094218. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362455 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Krafft C., Sergo V. Biomedical applications of Raman and infrared spectroscopy to diagnose tissues. Spectroscopy. 2006;20:195–218. doi: 10.1155/2006/738186. - DOI
-
- Fleischmann M., Hendra P.J., McQuillan A.J. Raman spectra of pyridine adsorbed at a silver electrode. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1974;26:163–166. doi: 10.1016/0009-2614(74)85388-1. - DOI
-
- Boginskaya I., Sedova M., Baburin A., Afanas’ev K., Zverev A., Echeistov V., Ryzhkov V., Rodionov I., Tonanaiskii B., Ryzhikov I., et al. SERS-active substrates nanoengineering based on e-beam evaporated self-assembled silver films. Appl. Sci. 2019;9:3988. doi: 10.3390/app9193988. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

