Murine Falcor/LL35 lncRNA Contributes to Glucose and Lipid Metabolism In Vitro and In Vivo
- PMID: 35740417
- PMCID: PMC9220108
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10061397
Murine Falcor/LL35 lncRNA Contributes to Glucose and Lipid Metabolism In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
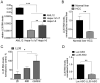
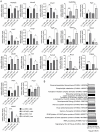
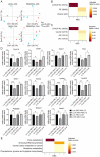
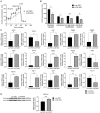
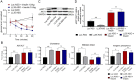
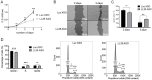
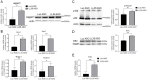
Glucose and lipid metabolism are crucial functional systems in eukaryotes. A large number of experimental studies both in animal models and humans have shown that long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play an important role in glucose and lipid metabolism. Previously, human lncRNA DEANR1/linc00261 was described as a tumor suppressor that regulates a variety of biological processes such as cell proliferation, apoptosis, glucose metabolism and tumorigenesis. Here we report that murine lncRNA Falcor/LL35, a proposed functional analog of human DEANR1/linc00261, is predominantly expressed in murine normal hepatocytes and downregulated in HCC and after partial hepatectomy. The application of high-throughput approaches such as RNA-seq, LC-MS proteomics, lipidomics and metabolomics analysis allowed changes to be found in the transcriptome, proteome, lipidome and metabolome of hepatocytes after LL35 depletion. We revealed that LL35 is involved in the regulation of glycolysis and lipid biosynthesis in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, LL35 affects Notch and NF-κB signaling pathways in normal hepatocytes. All observed changes result in the decrease in the proliferation and migration of hepatocytes. We demonstrated similar phenotype changes between murine LL35 and human linc00261 depletion in vitro and in vivo that opens the opportunity to translate results for LL35 from a liver murine model to possible functions of human lncRNA linc00261.
Keywords: glucose metabolism; hepatocyte; lipid metabolism; liver; long non-coding RNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Long Noncoding RNA LL35/Falcor Regulates Expression of Transcription Factor Foxa2 in Hepatocytes in Normal and Fibrotic Mouse Liver.Acta Naturae. 2019 Jul-Sep;11(3):66-74. doi: 10.32607/20758251-2019-11-3-66-74. Acta Naturae. 2019. PMID: 31720018 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Profile Analysis Reveals an Estrogen Induced LncRNA Associated with Lipid Metabolism and Carcass Traits in Chickens (Gallus Gallus).Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(5):1638-1658. doi: 10.1159/000494785. Epub 2018 Nov 1. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30384372
-
LINC00261: a burgeoning long noncoding RNA related to cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 May 22;21(1):274. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-01988-8. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 34022894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LINC00261 suppresses cell proliferation, invasion and Notch signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Biomark. 2018 Feb 14;21(3):575-582. doi: 10.3233/CBM-170471. Cancer Biomark. 2018. PMID: 29278875
-
Regulation of Glucose and Lipid Metabolism by Long Non-coding RNAs: Facts and Research Progress.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Jul 16;11:457. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00457. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 32765426 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

