Mediterranean Diet Adherence, Body Mass Index and Emotional Intelligence in Primary Education Students-An Explanatory Model as a Function of Weekly Physical Activity
- PMID: 35740809
- PMCID: PMC9221708
- DOI: 10.3390/children9060872
Mediterranean Diet Adherence, Body Mass Index and Emotional Intelligence in Primary Education Students-An Explanatory Model as a Function of Weekly Physical Activity
Abstract
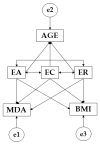
Adolescence is a key developmental period from a health, physical and psychological perspective. In view of this, the present research aimed to establish the relationship between emotional intelligence, Mediterranean diet adherence, BMI and age. In order to address this aim, (a) an explanatory model is developed of emotional intelligence and its relationship with Mediterranean diet adherence, BMI and age, and (b) the proposed structural model is examined via multi-group analysis as a function of whether students engage in more than three hours of physical activity a week. To this end, a quantitative, non-experimental (ex post facto), comparative and cross-sectional study was carried out with a sample of 567 students (11.10 ± 1.24). The instruments used were an ad hoc questionnaire, the KIDMED questionnaire and the TMMS-24. Outcomes reveal that participants who engage in more than three hours of physical activity a week score more highly for emotional intelligence than those who do not meet this criterion. Furthermore, it was also observed that, whilst the majority of the sample was physically active, improvement was required with regards to Mediterranean diet adherence.
Keywords: Mediterranean diet; body mass index; emotional intelligence; physical activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Brylka A., Wolke D., Ludyga S., Bilgin A., Spiegler J., Trower H., Gkiouleka A., Gerber M., Brand S., Grob A., et al. Physical activity, mental health, and well-being in very pre-term and term born adolescents: An individual participant data meta-analysis of two accelerometry studies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2021;18:1735. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18041735. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Morelli C., Avolio E., Galluccio A., Caparello G., Manes E., Ferraro S., Caruso A., De Rose D., Barone I., Adornetto C., et al. Nutrition education program and physical activity improve the adherence to the Mediterranean diet: Impact on inflammatory biomarker levels in healthy adolescents from the DIMENU longitudinal study. Front. Nutr. 2021;8:685247. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.685247. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

