Plasma Exosome-Derived microRNAs as Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Brazilian Pancreatic Cancer Patients
- PMID: 35740894
- PMCID: PMC9221134
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12060769
Plasma Exosome-Derived microRNAs as Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Brazilian Pancreatic Cancer Patients
Abstract
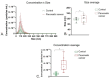
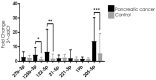
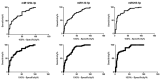
Pancreatic cancer represents one of the leading causes of oncological death worldwide. A combination of pancreatic cancer aggressiveness and late diagnosis are key factors leading to a low survival rate and treatment inefficiency, and early diagnosis is pursued as a critical factor for pancreatic cancer. In this context, plasma microRNAs are emerging as promising players due to their non-invasive and practical usage in oncological diagnosis and prognosis. Recent studies have showed some miRNAs associated with pancreatic cancer subtypes, or with stages of the disease. Here we demonstrate plasma exosome-derived microRNA expression in pancreatic cancer patients and healthy individuals from Brazilian patients. Using plasma of 65 pancreatic cancer patients and 78 healthy controls, plasma exosomes were isolated and miRNAs miR-27b, miR-125b-3p, miR-122-5p, miR-21-5p, miR-221-3p, miR-19b, and miR-205-5p were quantified by RT-qPCR. We found that miR-125b-3p, miR-122-5p, and miR-205-5p were statistically overexpressed in the plasma exosomes of pancreatic cancer patients compared to healthy controls. Moreover, miR-205-5p was significantly overexpressed in European descendants, in patients with tumor progression and in those who died from the disease, and diagnostic ability by ROC curve was 0.86. Therefore, we demonstrate that these three microRNAs are potential plasma exosome-derived non-invasive biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of Brazilian pancreatic cancer, demonstrating the importance of different populations and epidemiological bias.
Keywords: Brazil; exosome; microRNA; pancreatic cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Plasma miRNAs in diagnosis and prognosis of pancreatic cancer: A miRNA expression analysis.Gene. 2018 Oct 5;673:181-193. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.06.037. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29913239
-
Role of exosomal microRNA-125b-5p in conferring the metastatic phenotype among pancreatic cancer cells with different potential of metastasis.Life Sci. 2020 Aug 15;255:117857. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117857. Epub 2020 May 27. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32470446
-
Identification of a six-miRNA panel in serum benefiting pancreatic cancer diagnosis.Cancer Med. 2019 Jun;8(6):2810-2822. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2145. Epub 2019 Apr 21. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 31006985 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of exosome biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of breast cancer patients.Clin Transl Oncol. 2018 Jul;20(7):906-911. doi: 10.1007/s12094-017-1805-0. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Clin Transl Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29143228
-
Impact of exosome therapy on pancreatic cancer and its progression.Med Oncol. 2023 Jul 5;40(8):225. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02101-x. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37405480 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The systematic role of pancreatic cancer exosomes: distant communication, liquid biopsy and future therapy.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Jul 25;24(1):264. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03456-5. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 39054529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small RNA sequencing analysis of peptide-affinity isolated plasma extracellular vesicles distinguishes pancreatic cancer patients from non-affected individuals.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 7;13(1):9251. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36370-3. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37286718 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome applications for the diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: An update (Review).Oncol Rep. 2025 Jan;53(1):13. doi: 10.3892/or.2024.8846. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Oncol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39575479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating microRNAs as Potential Biomarkers in Pancreatic Cancer-Advances and Challenges.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 28;24(17):13340. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713340. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes colorectal cancer metastasis by excretion of miR-122-5p from cells via exosomes.iScience. 2023 Aug 19;26(9):107686. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107686. eCollection 2023 Sep 15. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37694140 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Cancer Society Cancer-Facts-and-Figures-2021. [(accessed on 15 March 2022)]. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

