Revisiting the miR-200 Family: A Clan of Five Siblings with Essential Roles in Development and Disease
- PMID: 35740906
- PMCID: PMC9221129
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12060781
Revisiting the miR-200 Family: A Clan of Five Siblings with Essential Roles in Development and Disease
Abstract
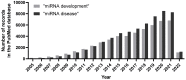
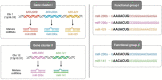
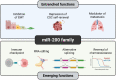
Over two decades of studies on small noncoding RNA molecules illustrate the significance of microRNAs (miRNAs/miRs) in controlling multiple physiological and pathological functions through post-transcriptional and spatiotemporal gene expression. Among the plethora of miRs that are essential during animal embryonic development, in this review, we elaborate the indispensable role of the miR-200 family (comprising miR-200a, -200b, 200c, -141, and -429) in governing the cellular functions associated with epithelial homeostasis, such as epithelial differentiation and neurogenesis. Additionally, in pathological contexts, miR-200 family members are primarily involved in tumor-suppressive roles, including the reversal of the cancer-associated epithelial-mesenchymal transition dedifferentiation process, and are dysregulated during organ fibrosis. Moreover, recent eminent studies have elucidated the crucial roles of miR-200s in the pathophysiology of multiple neurodegenerative diseases and tissue fibrosis. Lastly, we summarize the key studies that have recognized the potential use of miR-200 members as biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of cancers, elaborating the application of these small biomolecules in aiding early cancer detection and intervention.
Keywords: cancer-associated miRNAs; development; epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT); miR-200 family; miRNA/microRNA; neurodegenerative diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Roles of miR-200 family members in lung cancer: more than tumor suppressors.Future Oncol. 2018 Nov;14(27):2875-2886. doi: 10.2217/fon-2018-0155. Epub 2018 Sep 13. Future Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30208739 Review.
-
The microRNA-200 family: small molecules with novel roles in cancer development, progression and therapy.Oncotarget. 2015 Mar 30;6(9):6472-98. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3052. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25762624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory roles of the miR-200 family in neurodegenerative diseases.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Nov;119:109409. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109409. Epub 2019 Sep 10. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31518873 Review.
-
miRNA and mRNA expression profiling identifies members of the miR-200 family as potential regulators of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pterygium.Exp Eye Res. 2013 Oct;115:189-98. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2013.07.003. Epub 2013 Jul 19. Exp Eye Res. 2013. PMID: 23872359 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of serum miR-200a, miR-200b, and miR-200c as candidate biomarkers in epithelial ovarian cancer and their association with clinicopathological features.Clin Transl Oncol. 2015 Oct;17(10):779-87. doi: 10.1007/s12094-015-1303-1. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Clin Transl Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26063644
Cited by
-
Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Extracellular Vesicles on Inhibition of Hepatic Fibrosis by Delivering miR-200a.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2024 Jun;21(4):609-624. doi: 10.1007/s13770-024-00631-7. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2024. PMID: 38568409 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated MicroRNA-mRNA Sequencing Analysis Identifies Regulators and Networks Involved in Feline Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 15;26(14):6764. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146764. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40725010 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal miR-200c and miR-141 as cerebrospinal fluid biopsy biomarkers for the response to chemotherapy in primary central nervous system lymphoma.Discov Oncol. 2023 Nov 16;14(1):205. doi: 10.1007/s12672-023-00812-1. Discov Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37971595 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive treatment of diabetic endothelial dysfunction based on pathophysiological mechanism.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Feb 28;12:1509884. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1509884. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40093018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Helicobacter pylori-activated fibroblasts as a silent partner in gastric cancer development.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023 Dec;42(4):1219-1256. doi: 10.1007/s10555-023-10122-1. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023. PMID: 37460910 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ohno S. So Much “Junk” DNA in Our Genome. Brookhaven Symp. Biol. 1972;23:366–370. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

