TRPV6 Regulation by Cis-22a and Cholesterol
- PMID: 35740929
- PMCID: PMC9221249
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12060804
TRPV6 Regulation by Cis-22a and Cholesterol
Abstract
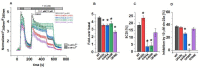
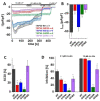
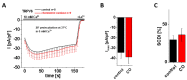
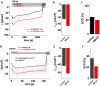
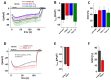
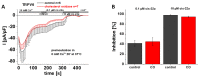
The highly calcium-selective transient receptor potential vanilloid-type channel TRPV6 is important for epithelial Ca2+ transport. Proper regulation of the inherently constitutively active TRPV6 channels is intricate in preserving Ca2+ homeostasis, whereby structural and functional data suggest that lipids hold an essential role. Altered expression levels or specific TRPV6 mutations may lead to diseases, hence, TRPV6 represents an interesting target for pharmacological modulation. Recent cryo-EM data identified that the specific TRPV6 blocker cis-22a binds, apart from the pore, to a site within the tetrameric channel that largely matches a lipid binding pocket, LBS-2. Therein, cis-22a may replace a lipid such as cholesterol that is bound in the open state. Based on site-directed mutagenesis and functional recordings, we identified and characterized a series of residues within LBS-2 that are essential for TRPV6 inhibition by cis-22a. Additionally, we investigated the modulatory potential of diverse cholesterol depletion efforts on TRPV6 activity. While LBS-2 mutants exhibited altered maximum currents, slow Ca2+-dependent inactivation (SCDI) as well as less inhibition by cis-22a, TRPV6 activity was resistant to cholesterol depletion. Hence, lipids other than cholesterol may predominate TRPV6 regulation when the channel is expressed in HEK293 cells.
Keywords: LBS-2; PIP2; TRPV6; cholesterol; lipid; maximum current; slow calcium dependent inactivation (SCDI).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

