Extracellular Vesicles Derived from MDA-MB-231 Cells Trigger Neutrophils to a Pro-Tumor Profile
- PMID: 35741003
- PMCID: PMC9221190
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11121875
Extracellular Vesicles Derived from MDA-MB-231 Cells Trigger Neutrophils to a Pro-Tumor Profile
Abstract
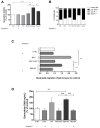
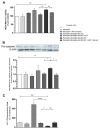
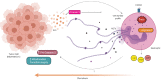
Immune system cells, including neutrophils, are recruited by the tumor microenvironment as a site of chronic inflammation and begin to favor tumor growth. Neutrophils present in the tumor site are called tumor-associated neutrophils (TAN) and can present two phenotypes: N1 (antitumor) or N2 (pro-tumor). Evidence shows the high capacity of immune system cells to interact with extracellular vesicles (Evs) released by tumor cells. Evs can modulate the phenotype of cells within the immune system, contributing to tumor development. Here, we investigated the role of MDA-MB-231-derived Evs upon the polarization of neutrophils towards an N2 phenotype and the underlying mechanisms. We observed that neutrophils treated with Evs released by MDA cells (MDA-Evs) had their half-life increased, increased their chemotactic capacity, and released higher levels of NETs and ROS than neutrophils treated with non-tumoral Evs. We also observed that neutrophils treated with MDA-Evs released increased IL-8, VEGF, MMP9, and increased expression of CD184, an N2-neutrophil marker. Finally, neutrophils treated with MDA-Evs increased tumor cell viability. Our results show that MDA-Evs induce an N2-like phenotype, and the blockage of phosphatidylserine by annexin-V may be an essential agent counter-regulating this effect.
Keywords: breast cancer; extracellular vesicles; inflammation; tumor-associated neutrophils.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest regarding the present study.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

