Characterization of Protein-Membrane Interactions in Yeast Autophagy
- PMID: 35741004
- PMCID: PMC9221364
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11121876
Characterization of Protein-Membrane Interactions in Yeast Autophagy
Abstract
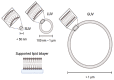
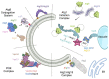
Cells rely on autophagy to degrade cytosolic material and maintain homeostasis. During autophagy, content to be degraded is encapsulated in double membrane vesicles, termed autophagosomes, which fuse with the yeast vacuole for degradation. This conserved cellular process requires the dynamic rearrangement of membranes. As such, the process of autophagy requires many soluble proteins that bind to membranes to restructure, tether, or facilitate lipid transfer between membranes. Here, we review the methods that have been used to investigate membrane binding by the core autophagy machinery and additional accessory proteins involved in autophagy in yeast. We also review the key experiments demonstrating how each autophagy protein was shown to interact with membranes.
Keywords: autophagy; membrane binding proteins; yeast.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

