Super-Resolution Imaging of Fas/CD95 Reorganization Induced by Membrane-Bound Fas Ligand Reveals Nanoscale Clustering Upstream of FADD Recruitment
- PMID: 35741037
- PMCID: PMC9221696
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11121908
Super-Resolution Imaging of Fas/CD95 Reorganization Induced by Membrane-Bound Fas Ligand Reveals Nanoscale Clustering Upstream of FADD Recruitment
Abstract
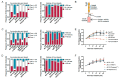
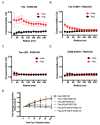
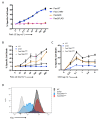
Signaling through the TNF-family receptor Fas/CD95 can trigger apoptosis or non-apoptotic cellular responses and is essential for protection from autoimmunity. Receptor clustering has been observed following interaction with Fas ligand (FasL), but the stoichiometry of Fas, particularly when triggered by membrane-bound FasL, the only form of FasL competent at inducing programmed cell death, is not known. Here we used super-resolution microscopy to study the behavior of single molecules of Fas/CD95 on the plasma membrane after interaction of Fas with FasL on planar lipid bilayers. We observed rapid formation of Fas protein superclusters containing more than 20 receptors after interactions with membrane-bound FasL. Fluorescence correlation imaging demonstrated recruitment of FADD dependent on an intact Fas death domain, with lipid raft association playing a secondary role. Flow-cytometric FRET analysis confirmed these results, and also showed that some Fas clustering can occur in the absence of FADD and caspase-8. Point mutations in the Fas death domain associated with autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome (ALPS) completely disrupted Fas reorganization and FADD recruitment, confirming structure-based predictions of the critical role that these residues play in Fas-Fas and Fas-FADD interactions. Finally, we showed that induction of apoptosis correlated with the ability to form superclusters and recruit FADD.
Keywords: CD95; Fas; PALM imaging; TNFR superfamily; receptor signaling; super-resolution microscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
R.M.S. is currently an employee of Novartis and owns Novartis stock.
Figures

References
-
- Wang L., Yang J.K., Kabaleeswaran V., Rice A.J., Cruz A.C., Park A.Y., Yin Q., Damko E., Jang S.B., Raunser S., et al. The Fas-FADD death domain complex structure reveals the basis of DISC assembly and disease mutations. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010;17:1324–1329. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1920. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stranges P.B., Watson J., Cooper C.J., Choisy-Rossi C.M., Stonebraker A.C., Beighton R.A., Hartig H., Sundberg J.P., Servick S., Kaufmann G., et al. Elimination of antigen-presenting cells and autoreactive T cells by Fas contributes to prevention of autoimmunity. Immunity. 2007;26:629–641. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.03.016. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

