Transcriptional Profiling of Insulin-like Growth Factor Signaling Components in Embryonic Lung Development and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
- PMID: 35741102
- PMCID: PMC9221724
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11121973
Transcriptional Profiling of Insulin-like Growth Factor Signaling Components in Embryonic Lung Development and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Abstract
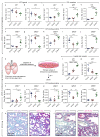
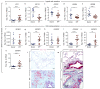
Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) signaling controls the development and growth of many organs, including the lung. Loss of function of Igf1 or its receptor Igf1r impairs lung development and leads to neonatal respiratory distress in mice. Although many components of the IGF signaling pathway have shown to be dysregulated in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), the expression pattern of such components in different cellular compartments of the developing and/or fibrotic lung has been elusive. In this study, we provide a comprehensive transcriptional profile for such signaling components during embryonic lung development in mice, bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice and in human IPF lung explants. During late gestation, we found that Igf1 is upregulated in parallel to Igf1r downregulation in the lung mesenchyme. Lung tissues derived from bleomycin-treated mice and explanted IPF lungs revealed upregulation of IGF1 in parallel to downregulation of IGF1R, in addition to upregulation of several IGF binding proteins (IGFBPs) in lung fibrosis. Finally, treatment of IPF lung fibroblasts with recombinant IGF1 led to myogenic differentiation. Our data serve as a resource for the transcriptional profile of IGF signaling components and warrant further research on the involvement of this pathway in both lung development and pulmonary disease.
Keywords: IGF1; IGF1R; bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; lung development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Regulation of the IGF1 signaling pathway is involved in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis induced by alveolar epithelial cell senescence and core fucosylation.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Jul 30;13(14):18852-18869. doi: 10.18632/aging.203335. Epub 2021 Jul 30. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34329195 Free PMC article.
-
Induced Pluripotent Stem-cells Inhibit Experimental Bleomycin-induced Pulmonary Fibrosis through Regulation of the Insulin-like Growth Factor Signaling.Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2022 Jun 18;21(3):263-272. doi: 10.18502/ijaai.v21i3.9800. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35822677
-
Loss of Fas signaling in fibroblasts impairs homeostatic fibrosis resolution and promotes persistent pulmonary fibrosis.JCI Insight. 2020 Dec 8;6(1):e141618. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.141618. JCI Insight. 2020. PMID: 33290280 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal expression of IGF-binding proteins, an initiating event in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis?Pathol Res Pract. 2010 Aug 15;206(8):537-43. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2010.03.010. Epub 2010 May 7. Pathol Res Pract. 2010. PMID: 20452131 Review.
-
MicroRNAs in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Transl Res. 2011 Apr;157(4):191-9. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2011.01.012. Epub 2011 Feb 4. Transl Res. 2011. PMID: 21420029 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Insulin Receptor Substrate Proteins in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Asthma: New Potential Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 4;23(17):10113. doi: 10.3390/ijms231710113. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CircDiaph3 influences PASMC apoptosis by regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway through IGF1R.3 Biotech. 2023 Oct;13(10):342. doi: 10.1007/s13205-023-03739-0. Epub 2023 Sep 11. 3 Biotech. 2023. PMID: 37705862 Free PMC article.
-
State of the Art in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Cells. 2022 Aug 11;11(16):2487. doi: 10.3390/cells11162487. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36010564 Free PMC article.
-
Highlights on Future Treatments of IPF: Clues and Pitfalls.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 1;25(15):8392. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158392. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms and markers of lung ageing in health and disease.Eur Respir Rev. 2025 Jul 23;34(177):240233. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0233-2024. Print 2025 Jul. Eur Respir Rev. 2025. PMID: 40701639 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Keselman A.C., Martin A., Scaglia P.A., Sanguineti N.M., Armando R., Gutiérrez M., Braslavsky D., Ballerini M.G., Ropelato M.G., Ramirez L., et al. A Homozygous Mutation in the Highly Conserved Tyr60 of the Mature IGF1 Peptide Broadens the Spectrum of IGF1 Deficiency. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2019;181:K43–K53. doi: 10.1530/EJE-19-0563. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yen Y.-C., Hsiao J.-R., Jiang S.S., Chang J.S., Wang S.-H., Shen Y.-Y., Chen C.-H., Chang I.-S., Chang J.-Y., Chen Y.-W. Insulin-like Growth Factor-Independent Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 3 Promotes Cell Migration and Lymph Node Metastasis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells by Requirement of Integrin Β1. Oncotarget. 2015;6:41837–41855. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5995. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

