Inflammatory and Cardiac Biomarkers in Relation with Post-Acute COVID-19 and Mortality: What We Know after Successive Pandemic Waves
- PMID: 35741183
- PMCID: PMC9222082
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12061373
Inflammatory and Cardiac Biomarkers in Relation with Post-Acute COVID-19 and Mortality: What We Know after Successive Pandemic Waves
Abstract
Background: Biomarkers were correlated with mortality in critically ill COVID-19 patients. No prediction tools exist for noncritically ill COVID-19 patients. We aimed to compare the independent prognostic value of inflammation and cardiac biomarkers for post-acute COVID-19 patients and the 30-day mortality rate in noncritically ill COVID-19 patients, as well as the relation with the virus variant involved.
Methods: This observational cohort study was conducted at an emergency clinical hospital between 1 October 2020 and 31 December 2021. We included consecutive patients with biomarkers determined within 24 h of presentation, followed up at least 30 days postdischarge.
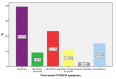
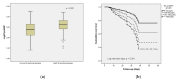
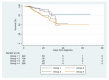
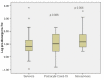
Results: Post-acute COVID-19 was diagnosed in 20.3% of the cases and the all-cause 30-day mortality rate was 35.1% among 978 patients infected with variants of concern. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (1.06 [95%CI, 1.01-1.11], p = 0.015) and NT-pro BNP were correlated with 30-daymortality, while the monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio (2.77 [95%CI, 1.10-6.94], p = 0.03) and NT-pro BNP (1.68 [95%CI, 1.00-2.84], p = 0.05) were correlated with post-acute COVID-19. High-sensitivity to troponin was associated with 30-day mortality (1.55 [95%CI, 1.00-2.42], p = 0.05). A Cox proportional-hazards model confirmed that NT-pro BNP was independently associated with mortality. NT-pro BNP remained independently associated with 30-day mortality during follow-up (1.29 [95%CI, 1.07-1.56], p = 0.007) after adjustment for confounders.
Conclusion: Inflammation and cardiac biomarkers, determined upon admission and predischarge, in a cohort of hospitalized noncritically ill COVID-19 patients throughout successive pandemic waves, showed a predictive value for post-acute COVID-19 and 30-day mortality.
Keywords: 30-day mortality; NT-pro BNP; high sensitivity cardiac troponin; inflammatory biomarkers; post-acute COVID-19; variants of concern.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Butt A.A., Dargham S.R., Chemaitelly H., Al Khal A., Tang P., Hasan M.R., Coyle P.V., Thomas A.G., Borham A.M., Concepcion E.G., et al. Severity of Illness in Persons Infected With the SARS-CoV-2 Delta Variant vs Beta Variant in Qatar. JAMA Int. Med. 2022;182:197–205. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.7949. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Post-COVID Conditions. [(accessed on 5 January 2022)]; Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/long-term-effects/index.html.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

