Sonographic Evaluation of Muscle Echogenicity for the Detection of Intensive Care Unit-Acquired Weakness: A Pilot Single-Center Prospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 35741188
- PMCID: PMC9221760
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12061378
Sonographic Evaluation of Muscle Echogenicity for the Detection of Intensive Care Unit-Acquired Weakness: A Pilot Single-Center Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
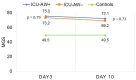
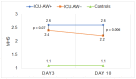
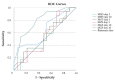
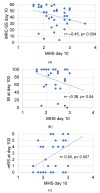
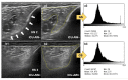
Qualitative assessment by the Heckmatt scale (HS) and quantitative greyscale analysis of muscle echogenicity were compared for their value in detecting intensive care unit-acquired weakness (ICU-AW). We performed muscle ultrasound (MUS) of eight skeletal muscles on day 3 and day 10 after ICU admission. We calculated the global mean greyscale score (MGS), the global mean z-score (MZS) and the global mean Heckmatt score (MHS). Longitudinal outcome was defined by the modified Rankin scale (mRS) and Barthel index (BI) after 100 days. In total, 652 ultrasound pictures from 38 critically ill patients (18 with and 20 without ICU-AW) and 10 controls were analyzed. Patients with ICU-AW had a higher MHS on day 10 compared to patients without ICU-AW (2.6 (0.4) vs. 2.2 (0.4), p = 0.006). The MHS was superior to ROC analysis (cut-off: 2.2, AUC: 0.79, p = 0.003, sensitivity 86%, specificity 60%) in detecting ICU-AW compared to MGS and MZS on day 10. The MHS correlated with the Medical Research Council sum score (MRC-SS) (r = -0.45, p = 0.004), the mRS (r = 0.45; p = 0.007) and BI (r = -0.38, p = 0.04) on day 100. Qualitative MUS analysis seems superior to quantitative greyscale analysis of muscle echogenicity for the detection of ICU-AW.
Keywords: ICU-AW; diagnostic ultrasound; muscle echogenicity; muscle weakness.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Muscular Ultrasound, Syndecan-1 and Procalcitonin Serum Levels to Assess Intensive Care Unit-Acquired Weakness.Can J Neurol Sci. 2019 Mar;46(2):234-242. doi: 10.1017/cjn.2018.390. Epub 2019 Feb 11. Can J Neurol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30739614 Clinical Trial.
-
[Diagnostic accuracy of muscle ultrasound and plasma monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 for ICU-acquired weakness in patients with sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022 Jan;34(1):12-17. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20211021-01531. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022. PMID: 35307054 Chinese.
-
Prospective ultrasonographic evaluation of femoral and vastus intermedius muscles as predictors of ICU-acquired weakness in critically ill patients.J Ultrasound. 2025 Jun;28(2):447-454. doi: 10.1007/s40477-025-01013-y. Epub 2025 Apr 22. J Ultrasound. 2025. PMID: 40261598 Free PMC article.
-
Intensive care unit-acquired weakness: unanswered questions and targets for future research.F1000Res. 2019 Apr 17;8:F1000 Faculty Rev-508. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.17376.1. eCollection 2019. F1000Res. 2019. PMID: 31069055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of mechanical ventilation and pulmonary rehabilitation in patients with ICU-acquired weakness: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Sep;10(9):9594-9606. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-1928. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 34628885
Cited by
-
Ultrasonographic Features of Muscular Weakness and Muscle Wasting in Critically Ill Patients.J Clin Med. 2023 Dec 20;13(1):26. doi: 10.3390/jcm13010026. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38202033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Intensive Care Unit-Acquired Weakness and Critical Illness Myopathy: A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 14;24(6):5516. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065516. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Muscle Changes Assessed by Ultrasonography on Muscle Strength and Functioning after ICU Discharge: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024 Jul 11;21(7):908. doi: 10.3390/ijerph21070908. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39063485 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and feasibility of 5G-based remote interactive ultrasound training in critical care.BMC Med Educ. 2024 May 8;24(1):514. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-05485-0. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 38720299 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Developing a reliable and convenient methodology for ultrasound muscle assessment in critically ill patients: A reliability study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Apr 25;104(17):e42263. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042263. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40295247 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Garnacho-Montero J., Madrazo-Osuna J., Garcia-Garmendia J.L., Ortiz-Leyba C., Jiménez-Jiménez F., Barrero-Almodóvar A., Garnacho-Montero M., Moyano-Del-Estad M. Critical illness polyneuropathy: Risk factors and clinical consequences. A cohort study in septic patients. Intensive Care Med. 2001;27:1288–1296. doi: 10.1007/s001340101009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Garnacho-Montero J., Amaya-Villar R., García-Garmendía J.L., Madrazo-Osuna J., Ortiz-Leyba C. Effect of critical illness polyneuropathy on the withdrawal from mechanical ventilation and the length of stay in septic patients. Crit. Care Med. 2005;33:349–354. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000153521.41848.7E. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

