Our Experience in Using the Endovascular Therapy in the Management of Hemorrhages in Obstetrics and Gynecology
- PMID: 35741246
- PMCID: PMC9222048
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12061436
Our Experience in Using the Endovascular Therapy in the Management of Hemorrhages in Obstetrics and Gynecology
Abstract
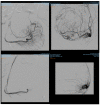
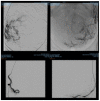
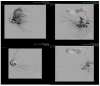
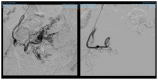
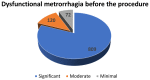
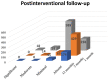
(1) Background: A quarter of maternal deaths are caused by post-partum hemorrhage; hence obstetric bleeding is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality among women. Pelvic artery embolization (PAE) represents a minimally invasive interventional procedure which plays an important role in conservative management of significant bleeding in Obstetrics and Gynecology. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect and the complications of PAE in patients with significant vaginal bleeding with different obstetrical and gynecological pathologies. (2) Methods: We conducted an observational, retrospective study on 1135 patients who presented to the University Emergency Hospital of Bucharest with vaginal bleeding of various etiology treated with endovascular therapy. All the patients included in the study presented vaginal hemorrhage that was caused by: uterine leiomyomas, genital tract malignancies, ectopic pregnancy, arterio-venous mal-formations and other obstetrical causes. We excluded patients with uncontrolled high blood pressure, severe hepatic impairment, congestive heart failure, renal failure or ventricular arrhythmias. (3) Results: Bleeding was caused in 88.19% of cases by uterine leiomyomas (n = 1001), 7.84% (n = 89) by cervical cancer, 2.29% by ectopic pregnancy (n = 26), 1.23% by arteriovenous malformation (n = 14) and 0.52% by major hemorrhage of obstetrical causes. Endovascular procedures were used in all the cases. In patients with uterine leiomyomas, supra-selective uterine arteries embolization was used. In 97% (n = 1101) of patients, bleeding was stopped after the first attempt of PAE. 3% (n = 34) needed a second embolization. In 12 of 14 cases of AVM, PAE was successful, two other cases needed reintervention; (4) Conclusions: Endovascular procedures represent a major therapy method for both acute and chronic hemorrhage in Obstetrics and Gynecology. It can be used in post-partum or post-traumatic causes of vaginal bleeding, but also in patients with chronic hemorrhage from uterine leiomyomas or inoperable genital malignancies or even as a preoperative adjuvant in cases of voluminous uterine fibroids or invasive malignant tumors, aiming to reduce intraoperative hemorrhage.
Keywords: endovascular therapy; management; vaginal hemorrhage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Endovascular management of massive post-partum haemorrhage in abnormal placental implantation deliveries.Eur Radiol. 2016 Jun;26(6):1620-30. doi: 10.1007/s00330-015-4001-z. Epub 2015 Sep 15. Eur Radiol. 2016. PMID: 26373762
-
The efficacy of pelvic arterial embolisation for the treatment in massive vaginal haemorrhage in obstetric and gynaecological emergencies: a single-centre experience.J Obstet Gynaecol. 2019 Aug;39(6):774-781. doi: 10.1080/01443615.2019.1586858. Epub 2019 Apr 25. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2019. PMID: 31023116
-
The management of uterine leiomyomas.J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2015 Feb;37(2):157-178. doi: 10.1016/S1701-2163(15)30338-8. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2015. PMID: 25767949
-
Transcatheter endovascular techniques for management of obstetrical and gynecologic emergencies.Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2009 Jun;12(2):139-47. doi: 10.1053/j.tvir.2009.08.007. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2009. PMID: 19853231 Review.
-
Uterine artery embolization: the role in obstetrics and gynecology.Clin Imaging. 2001 Jul-Aug;25(4):288-95. doi: 10.1016/s0899-7071(01)00307-2. Clin Imaging. 2001. PMID: 11566093 Review.
Cited by
-
The clinical application of transarterial embolization via radial artery in hemorrhagic diseases in obstetrics and gynecology.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Oct 19;10:1273179. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1273179. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37928466 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

