Recent Advances in Progresses and Prospects of IL-37 in Central Nervous System Diseases
- PMID: 35741608
- PMCID: PMC9221119
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci12060723
Recent Advances in Progresses and Prospects of IL-37 in Central Nervous System Diseases
Abstract
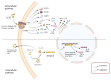
Interleukin-37 (IL-37) is an effective anti-inflammatory factor and acts through intracellular and extracellular pathways, inhibiting the effects of other inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1β, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), thereby exerting powerful anti-inflammatory effects. In numerous recent studies, the anti-inflammatory effects of IL-37 have been described in many autoimmune diseases, colitis, and tumors. However, the current research on IL-37 in the field of the central nervous system (CNS) is not only less, but mainly for clinical research and little discussion of the mechanism. In this review, the role of IL-37 and its associated inflammatory factors in common CNS diseases are summarized, and their therapeutic potential in CNS diseases identified.
Keywords: Interleukin-37; anti-inflammatory; central nervous system diseases; cytokines; inflammatory.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bello R.O., Chin V.K., Abd Rachman Isnadi M.F., Abd Majid R., Atmadini Abdullah M., Lee T.Y., Amiruddin Zakaria Z., Hussain M.K., Basir R. The Role, Involvement and Function(s) of Interleukin-35 and Interleukin-37 in Disease Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018;19:1149. doi: 10.3390/ijms19041149. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kumar S., McDonnell P.C., Lehr R., Tierney L., Tzimas M.N., Griswold D.E., Capper E.A., Tal-Singer R., Wells G.I., Doyle M.L., et al. Identification and initial characterization of four novel members of the interleukin-1 family. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:10308–10314. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.14.10308. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

