The Effect of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Error Rates in the Distractor-Induced Deafness Paradigm
- PMID: 35741623
- PMCID: PMC9220866
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci12060738
The Effect of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Error Rates in the Distractor-Induced Deafness Paradigm
Abstract
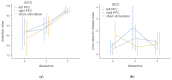
To further understand how consciousness emerges, certain paradigms inducing distractor-induced perceptual impairments are promising. Neuro-computational models explain the inhibition of conscious perception of targets with suppression of distractor information when the target and distractor share the same features. Because these gating mechanisms are controlled by the prefrontal cortex, transcranial direct current stimulation of this specific region is expected to alter distractor-induced effects depending on the presence and number of distractors. To this end, participants were asked to perform an auditory variant of the distractor-induced blindness paradigm under frontal transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS). Results show the expected distractor-induced deafness effects in a reduction of target detection depending on the number of distractors. While tDCS had no significant effects on target detection per se, error rates due to missed cues are increased under stimulation. Thus, while our variant led to successful replication of behavioral deafness effects, the results under tDCS stimulation indicate that the chosen paradigm may have difficulty too low to respond to stimulation. That the error rates nevertheless led to a tDCS effect may be due to the divided attention between the visual cue and the auditory target.
Keywords: attention; conscious perception; distractor-induced deafness; transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources