Genome-Wide RNA Sequencing Analysis in Human Dermal Fibroblasts Exposed to Low-Dose Ultraviolet A Radiation
- PMID: 35741736
- PMCID: PMC9222854
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13060974
Genome-Wide RNA Sequencing Analysis in Human Dermal Fibroblasts Exposed to Low-Dose Ultraviolet A Radiation
Abstract
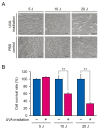
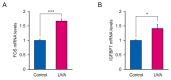
Ultraviolet A (UVA) radiation can pass through the epidermis and reach the dermal skin layer, contributing to photoaging, DNA damage, and photocarcinogenesis in dermal fibroblasts. High-dose UVA exposure induces erythema, whereas low-dose, long-term UVA exposure causes skin damage and cell senescence. Biomarkers for evaluating damage caused by low-dose UVA in fibroblasts are lacking, making it difficult to develop therapeutic agents for skin aging and aging-associated diseases. We performed RNA-sequencing to investigate gene and pathway alterations in low-dose UVA-irradiated human skin-derived NB1RGB primary fibroblasts. Differentially expressed genes were identified and subjected to Gene Ontology and reactome pathway analysis, which revealed enrichment in genes in the senescence-associated secretory phenotype, apoptosis, respiratory electron transport, and transcriptional regulation by tumor suppressor p53 pathways. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 (IGFBP7) showed the lowest p-value in RNA-sequencing analysis and was associated with the senescence-associated secretory phenotype. Protein-protein interaction analysis revealed that Fos proto-oncogene had a high-confidence network with IGFBP7 as transcription factor of the IGFBP7 gene among SASP hit genes, which were validated using RT-qPCR. Because of their high sensitivity to low-dose UVA radiation, Fos and IGFBP7 show potential as biomarkers for evaluating the effect of low-dose UVA radiation on dermal fibroblasts.
Keywords: Fos; IGFBP7; biomarker; differentially expressed gene; low-dose UVA; senescence-associated secretory phenotype; ultraviolet A.
Conflict of interest statement
The sponsors, C’BON COSMETICS Co., Ltd., had no role in the design, execution, interpretation, or writing of the study. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Effects of baicalin against UVA-induced photoaging in skin fibroblasts.Am J Chin Med. 2014;42(3):709-27. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X14500463. Am J Chin Med. 2014. PMID: 24871661
-
IL-1 receptor antagonist attenuates MAP kinase/AP-1 activation and MMP1 expression in UVA-irradiated human fibroblasts induced by culture medium from UVB-irradiated human skin keratinocytes.Int J Mol Med. 2005 Dec;16(6):1117-24. Int J Mol Med. 2005. PMID: 16273295
-
Ultraviolet A-induced cathepsin K expression is mediated via MAPK/AP-1 pathway in human dermal fibroblasts.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 21;9(7):e102732. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102732. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25048708 Free PMC article.
-
New insights in photoaging, UVA induced damage and skin types.Exp Dermatol. 2014 Oct;23 Suppl 1:7-12. doi: 10.1111/exd.12388. Exp Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 25234829 Review.
-
Sunscreens containing the broad-spectrum UVA absorber, Mexoryl SX, prevent the cutaneous detrimental effects of UV exposure: a review of clinical study results.Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2008 Aug;24(4):164-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0781.2008.00365.x. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2008. PMID: 18717957 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

