The Efficacy of Machine-Learning-Supported Smart System for Heart Disease Prediction
- PMID: 35742188
- PMCID: PMC9222326
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare10061137
The Efficacy of Machine-Learning-Supported Smart System for Heart Disease Prediction
Abstract
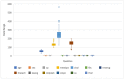
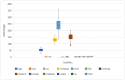
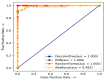
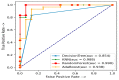
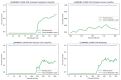
The disease may be an explicit status that negatively affects human health. Cardiopathy is one of the common deadly diseases that is attributed to unhealthy human habits compared to alternative diseases. With the help of machine learning (ML) algorithms, heart disease can be noticed in a short time as well as at a low cost. This study adopted four machine learning models, such as random forest (RF), decision tree (DT), AdaBoost (AB), and K-nearest neighbor (KNN), to detect heart disease. A generalized algorithm was constructed to analyze the strength of the relevant factors that contribute to heart disease prediction. The models were evaluated using the datasets Cleveland, Hungary, Switzerland, and Long Beach (CHSLB), and all were collected from Kaggle. Based on the CHSLB dataset, RF, DT, AB, and KNN models predicted an accuracy of 99.03%, 96.10%, 100%, and 100%, respectively. In the case of a single (Cleveland) dataset, only two models, namely RF and KNN, show good accuracy of 93.437% and 97.83%, respectively. Finally, the study used Streamlit, an internet-based cloud hosting platform, to develop a computer-aided smart system for disease prediction. It is expected that the proposed tool together with the ML algorithm will play a key role in diagnosing heart diseases in a very convenient manner. Above all, the study has made a substantial contribution to the computation of strength scores with significant predictors in the prognosis of heart disease.
Keywords: AdaBoost; KNN; decision tree; heart disease; prediction; random forest; smart system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Cardiometabolic Diseases. 2022. [(accessed on 1 March 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases...
-
- Ayon S.I., Islam M., Hossain R. Coronary Artery Heart Disease Prediction: A Comparative Study of Computational Intelligence Techniques. IETE J. Res. 2020:1–20. doi: 10.1080/03772063.2020.1713916. - DOI
-
- Ayon S.I., Islam M.M. Diabetes prediction: A deep learning approach. Int. J. Inf. Eng. Electron. Bus. 2019;11:21–27.
-
- Manogaran G., Varatharajan R., Priyan M.K. Hybrid Recommendation System for Heart Disease Diagnosis based on Multiple Kernel Learning with Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2017;77:4379–4399. doi: 10.1007/s11042-017-5515-y. - DOI
-
- Hasan M.K., Islam M.M., Hashem M.M.A. Mathematical model development to detect breast cancer using multigene genetic programming; Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Informatics, Electronics and Vision (ICIEV); Dhaka, Bangladesh. 13–14 May 2016; pp. 574–579.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

