Assessing Patient Experience and Attitude: BSC-PATIENT Development, Translation, and Psychometric Evaluation-A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 35742393
- PMCID: PMC9223066
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19127149
Assessing Patient Experience and Attitude: BSC-PATIENT Development, Translation, and Psychometric Evaluation-A Cross-Sectional Study
Erratum in
-
Correction: Amer et al. Assessing Patient Experience and Attitude: BSC-PATIENT Development, Translation, and Psychometric Evaluation-A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7149.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Sep 28;19(19):12319. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191912319. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36232286 Free PMC article.
Abstract
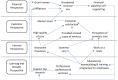
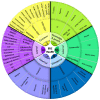
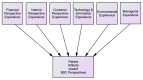
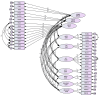
Health care organizations (HCO) did not consider engaging patients in balanced scorecard (BSC) implementations to evaluate their performance. This paper aims to develop an instrument to engage patients in assessing BSC perspectives (BSC-PATIENT) and customize it for Palestinian hospitals. Two panels of experts participated in the item generation of BSC-PATIENT. Translation was performed based on guidelines. Pretesting was performed for 30 patients at one hospital. Then, 1000 patients were recruited at 14 hospitals between January and October 2021. Construct validity was tested through exploratory factor analysis (EFA) and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA). Additionally, the composite reliability (CR), interitem correlation (IIC), and corrected item total correlation (CITC) were assessed to find redundant and low correlated items. As a result, the scales had a highly adequate model fit in the EFA and CFA. The final best fit model in CFA comprised ten constructs with 36 items. In conclusion, BSC-PATIENT is the first self-administered questionnaire specifically developed to engage patients in BSC and will allow future researchers to evaluate the impact of patient experience on attitudes toward BSC perspectives, as well as to compare the differences based on patient and hospital characteristics.
Keywords: balanced scorecard; hospital; patient engagement; performance evaluation; quality; satisfaction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Meena K., Thakkar J. Development of Balanced Scorecard for Healthcare Using Interpretive Structural Modeling and Analytic Network Process. J. Adv. Manag. Res. 2014;11:232–256. doi: 10.1108/JAMR-12-2012-0051. - DOI
-
- Barghouthi M., Lennock J. Health in Palestine: Potential and Challenges. Palestine Economic Policy Research Institute (MAS); Jerusalem, Israel: 1997.
-
- PMOH Health Annual Report, Palestine 2020. May, 2021. [(accessed on 10 April 2022)]. Available online: https://Moh.Ps.
-
- Sabella A.R., Kashou R., Omran O. Assessing Quality of Management Practices in Palestinian Hospitals. Int. J. Organ. Anal. 2015;23:213–232. doi: 10.1108/IJOA-03-2014-0747. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

