Long-Term Kinetics of Serological Antibodies against Vibrio cholerae Following a Clinical Cholera Case: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35742404
- PMCID: PMC9223532
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19127141
Long-Term Kinetics of Serological Antibodies against Vibrio cholerae Following a Clinical Cholera Case: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Approximately 2.9 million people worldwide suffer from cholera each year, many of whom are destitute. However, understanding of immunity against cholera is still limited. Several studies have reported the duration of antibodies following cholera; however, systematic reviews including a quantitative synthesis are lacking.
Objective: To meta-analyze cohort studies that have evaluated vibriocidal, cholera toxin B subunit (CTB), and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) antibody levels following a clinical cholera case.
Methods: Design: Systematic review and meta-analysis. We searched PubMed and Web of science for studies assessing antibodies against Vibrio cholerae in cohorts of patients with clinical cholera. Two authors independently extracted data and assessed the quality of included studies. Random effects models were used to pool antibody titers in adults and older children (aged ≥ 6 years). In sensitivity analysis, studies reporting data on young children (2-5 years) were included.
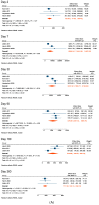
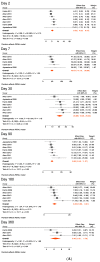
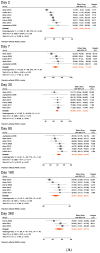
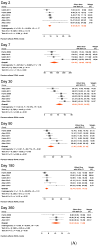
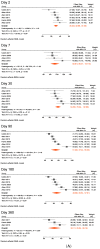
Results: Nine studies met our inclusion criteria for systematic review and seven for meta-analysis. The pooled mean of vibriocidal antibody titers in adults and older children (aged ≥ 6 years) was 123 on day 2 post-symptom onset, which sharply increased on day 7 (pooled mean = 6956) and gradually waned to 2247 on day 30, 578 on day 90, and 177 on day 360. Anti-CTB IgA antibodies also peaked on day 7 (pooled mean = 49), followed by a rapid decrease on day 30 (pooled mean = 21), and further declined on day 90 (pooled mean = 10), after which it plateaued from day 180 (pooled mean = 8) to 360 (pooled mean = 6). Similarly, anti-CTB IgG antibodies peaked in early convalescence between days 7 (pooled mean = 65) and 30 (pooled mean = 69), then gradually waned on days 90 (pooled mean = 42) and 180 (pooled mean = 30) and returned to baseline on day 360 (pooled mean = 24). Anti-LPS IgA antibodies peaked on day 7 (pooled mean = 124), gradually declined on day 30 (pooled mean = 44), which persisted until day 360 (pooled mean = 10). Anti LPS IgG antibodies peaked on day 7 (pooled mean = 94). Thereafter, they decreased on day 30 (pooled mean = 85), and dropped further on days 90 (pooled mean = 51) and 180 (pooled mean = 47), and returned to baseline on day 360 (pooled mean = 32). Sensitivity analysis including data from young children (aged 2-5 years) showed very similar findings as in the primary analysis.
Conclusions: This study confirms that serological antibody (vibriocidal, CTB, and LPS) titers return to baseline levels within 1 year following clinical cholera, i.e., before the protective immunity against subsequent cholera wanes. However, this decay should not be interpreted as waning immunity because immunity conferred by cholera against subsequent disease lasts 3-10 years. Our study provides evidence for surveillance strategies and future research on vaccines and also demonstrates the need for further studies to improve our understanding of immunity against cholera.
Keywords: antibodies; cholera; cholera toxin B; immunity; immunoglobulin; lipopolysaccharide; vibriocidal; waning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Antibody tests for identification of current and past infection with SARS-CoV-2.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Nov 17;11(11):CD013652. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013652.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36394900 Free PMC article.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Eliciting adverse effects data from participants in clinical trials.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 16;1(1):MR000039. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000039.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29372930 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Effects of a gluten-reduced or gluten-free diet for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 24;2(2):CD013556. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013556.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35199850 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Longterm kinetics of vibriocidal antibody responses after V. cholerae infection in the Democratic Republic of Congo.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Apr 11:2025.02.26.25322966. doi: 10.1101/2025.02.26.25322966. medRxiv. 2025. Update in: J Infect Dis. 2025 Jul 22:jiaf382. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaf382. PMID: 40061355 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Seroconversion and Kinetics of Vibriocidal Antibodies during the First 90 Days of Re-Vaccination with Oral Cholera Vaccine in an Endemic Population.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Apr 8;12(4):390. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12040390. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38675772 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Cholera. [(accessed on 24 May 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/cholera#tab=tab_1.
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Cholera vaccines: WHO position paper—August 2017. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 2017;92:477–498. - PubMed
-
- Alam M., Sultana M., Nair G.B., Siddique A.K., Hasan N.A., Sack R.B., Sack D.A., Ahmed K.U., Sadique A., Watanabe H., et al. Viable but nonculturable Vibrio cholerae O1 in biofilms in the aquatic environment and their role in cholera transmission. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2007;104:17801–17806. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0705599104. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

