Insulin Resistance and Urolithiasis as a Challenge for a Dietitian
- PMID: 35742405
- PMCID: PMC9223170
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19127160
Insulin Resistance and Urolithiasis as a Challenge for a Dietitian
Abstract
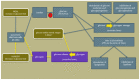
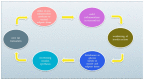
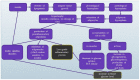
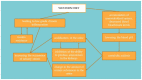
Many obesity and diet-related diseases have been observed in recent years. Insulin resistance (IR), a state of tissue resistance to insulin due to its impaired function, is a common coexisting condition. The most important predisposing factors are excessive visceral fat and chronic low-grade inflammatory response. However, IR's pathogenesis is not fully understood. Hence, the diagnosis of IR should be carried out carefully because many different diagnostic paths do not always give equivalent results. An additional disease that is often associated with IR is urolithiasis. The common feature of these two conditions is metabolic acidosis and mild inflammation. A patient diagnosed with IR and urolithiasis is a big challenge for a dietitian. It is necessary to check a thorough dietary history, make an appropriate anthropometric measurement, plan a full-fledged diet, and carry out the correct nutritional treatment. It is also essential to conduct proper laboratory diagnostics to plan nutritional treatment, which is often a big challenge for dietitians. The diet's basic assumptions are based on the appropriate selection of carbohydrates, healthy fats, and wholesome protein sources. It is also essential to properly compose meals, prepare them, and plan physical activities tailored to the abilities. The study aims to summarise the necessary information on IR with concomitant urolithiasis, which may be helpful in dietary practice.
Keywords: diet; dietitian; inflammation; insulin; insulin resistance; urolithiasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oral AGE restriction ameliorates insulin resistance in obese individuals with the metabolic syndrome: a randomised controlled trial.Diabetologia. 2016 Oct;59(10):2181-92. doi: 10.1007/s00125-016-4053-x. Epub 2016 Jul 29. Diabetologia. 2016. PMID: 27468708 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A high ratio of dietary n-3/n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids improves obesity-linked inflammation and insulin resistance through suppressing activation of TLR4 in SD rats.Nutr Res. 2013 Oct;33(10):849-58. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2013.07.004. Epub 2013 Aug 9. Nutr Res. 2013. PMID: 24074743
-
Dissociation of hepatic insulin resistance from susceptibility of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease induced by a high-fat and high-carbohydrate diet in mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014 Mar;306(6):G496-504. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00291.2013. Epub 2014 Jan 16. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24436353 Free PMC article.
-
[Simple obesity in children. A study on the role of nutritional factors].Med Wieku Rozwoj. 2006 Jan-Mar;10(1):3-191. Med Wieku Rozwoj. 2006. PMID: 16733288 Review. Polish.
-
Metabolic consequences of obesity and insulin resistance in polycystic ovary syndrome: diagnostic and methodological challenges.Nutr Res Rev. 2017 Jun;30(1):97-105. doi: 10.1017/S0954422416000287. Epub 2017 Feb 22. Nutr Res Rev. 2017. PMID: 28222828 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of vitamin D supplementation on glucose and lipid metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and risk factors for insulin resistance.World J Diabetes. 2023 Oct 15;14(10):1514-1523. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i10.1514. World J Diabetes. 2023. PMID: 37970127 Free PMC article.
-
Key Therapeutic Targets to Treat Hyperglycemia-Induced Atherosclerosis Analyzed Using a Petri Net-Based Model.Metabolites. 2023 Dec 8;13(12):1191. doi: 10.3390/metabo13121191. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 38132873 Free PMC article.
-
Ghrelin and Leptin among Patients with Urolithiasis with Concomitant Hyperuricemia and Metabolic Syndrome.Biomedicines. 2023 Jan 19;11(2):285. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020285. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36830821 Free PMC article.
-
Inverted V-shaped association between atherogenic index of plasma and kidney stone risk: results from NHANES 2011-2018.Transl Androl Urol. 2025 Apr 30;14(4):953-963. doi: 10.21037/tau-24-605. Epub 2025 Apr 27. Transl Androl Urol. 2025. PMID: 40376532 Free PMC article.
-
High-Fructose Diet-Induced Hyperuricemia Accompanying Metabolic Syndrome-Mechanisms and Dietary Therapy Proposals.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Feb 17;20(4):3596. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20043596. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36834291 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gupta A., Gupta V. Metabolic syndrome: What are the risks for humans? BioSci. Trends. 2010;4:204–212. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

