Electrostatic Spray Disinfection Using Nano-Engineered Solution on Frequently Touched Surfaces in Indoor and Outdoor Environments
- PMID: 35742489
- PMCID: PMC9223583
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19127241
Electrostatic Spray Disinfection Using Nano-Engineered Solution on Frequently Touched Surfaces in Indoor and Outdoor Environments
Abstract
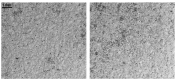
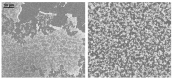
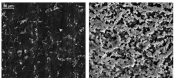
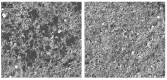
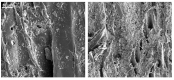
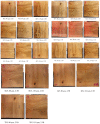
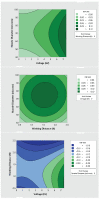
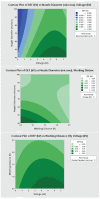
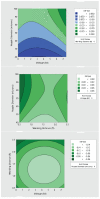
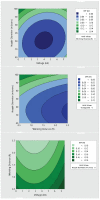
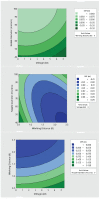
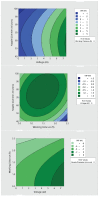
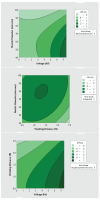
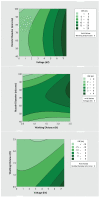
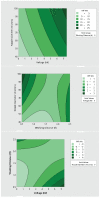
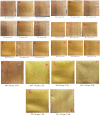
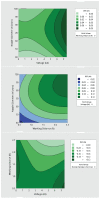
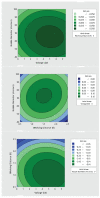
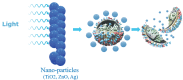
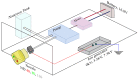
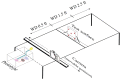
The COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in high demand for disinfection technologies. However, the corresponding spray technologies are still not completely optimized for disinfection purposes. There are important problems, like the irregular coverage and dripping of disinfectant solutions on hard and vertical surfaces. In this study, we highlight two major points. Firstly, we discuss the effectiveness of the electrostatic spray deposition (ESD) of nanoparticle-based disinfectant solutions for systematic and long-lasting disinfection. Secondly, we show that, based on the type of material of the substrate, the effectiveness of ESD varies. Accordingly, 12 frequently touched surface materials were sprayed using a range of electrostatic spray system parameters, including ion generator voltage, nozzle spray size and distance of spray. It was observed that for most cases, the surfaces become completely covered with the nanoparticles within 10 s. Acrylic, Teflon, PVC, and polypropylene surfaces show a distinct effect of ESD and non-ESD sprays. The nanoparticles form a uniform layer with better surface coverage in case of electrostatic deposition. Quantitative variations and correlations show that 1.5 feet of working distance, an 80 μm spray nozzle diameter and an ion generator voltage of 3-7 kV ensures a DEF (differential electric field) that corresponds to an optimized charge-to-mass ratio, ensuring efficient coverage of nanoparticles.
Keywords: COVID-19; disinfection; electrostatic spray deposition; fomites; nano-disinfectant; pathogens.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures












References
-
- Colaneri M., Seminari E., Novati S., Asperges E., Biscarini S., Piralla A., Percivalle E., Cassaniti I., Baldanti F., Bruno R., et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 RNA contamination of inanimate surfaces and virus viability in a health care emergency unit. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020;26:1094.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.05.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

