Diversity of Toxigenic Fungi in Livestock and Poultry Feedstuffs
- PMID: 35742499
- PMCID: PMC9224174
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19127250
Diversity of Toxigenic Fungi in Livestock and Poultry Feedstuffs
Abstract
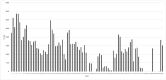
The purpose of this study was to discover how abundant toxigenic fungi and mycotoxins are in animal feedstuff samples. A total of ninety samples representing various types of animal feedstuff samples were collected from ninety sites in Egypt. Isolation, identification, and determination of mycotoxins (aflatoxins B1, B2, G1, G2, and ochratoxin A) were performed. The results revealed that 79 (87.77%) of the samples were contaminated with fungi, and 1.1 × 105 CFU/g were recovered, including 41 fungal species belonging to 18 genera, such as Zygomycota, which was represented by three species (7.31% of the total species number), teleomorphic Ascomycota (10 species, 24.39%), and anamorphic Ascomycota (28 species, 69.29%). When taxonomically investigated, these species were categorized into 2 phyla, 4 classes, 6 orders, and 12 families (one of them with an uncertain position). Moreover, the genus Aspergillus exhibited 16 species (39.02%). Notably, site no. 6 showed the highest Margalef species richness index at 10.87 followed by site no. 4, while the Shannon diversity index (H) of the recovered taxa was 2.20. Based on the frequency of occurrence, Aspergillus flavus recorded the highest percentage (65.56%) followed by A. niger (50%) and Penicillium chrysogenum (40%). Genus Aspergillus was recorded in 75 samples (88.33%), while Penicillium appeared only in 43 samples, accounting for 47.77% out of 90 samples. The High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis showed that aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) was recorded in two animal feedstuff samples at a ratio of 0.851 and 1.363 µg/kg, While AFB2 was discovered in only one animal feedstuff sample at a ratio of 0.479 g/kg. The aflatoxins levels in the positive samples (AFB1 and AFB2) Beef cattle sample components were below the permissible limit for animal feedstuff which is (20 g/kg). Although aflatoxins were found in certain samples, the amounts were much below the maximum residue limits (MRLs) defined by the international authorities or Egyptian guidelines. toxigenic fungi found in contaminated animal feed samples pose a major threat to animal and poultry health, productivity, and even human health. Therefore, periodic monitoring is an excellent way to keep track of their existence and mitigate their hazards.
Keywords: Aspergillus species; HPLC; aflatoxins; animal feedstuff samples; fungi; mycotoxins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aflatoxins and ochratoxin A in stored barley grain in Spain and impact of PCR-based strategies to assess the occurrence of aflatoxigenic and ochratoxigenic Aspergillus spp.Int J Food Microbiol. 2011 Sep 15;149(2):118-26. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2011.06.006. Epub 2011 Jun 24. Int J Food Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21741104
-
Fungal flora and aflatoxin contamination of feedstuff samples in Beida Governorate, Libya.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 1996;41(1):53-60. doi: 10.1007/BF02816341. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 1996. PMID: 9090825
-
Occurrence of Toxigenic Fungi and Mycotoxins on Root Herbs from Chinese Markets.J Food Prot. 2018 May;81(5):754-761. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-17-405. J Food Prot. 2018. PMID: 29620485
-
[Legal Regulation and Analytical Method for Mycotoxin in Japan].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2025;145(2):117-120. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.24-00164-5. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2025. PMID: 39894480 Review. Japanese.
-
Mycotoxin Contamination of Rice in China.J Food Sci. 2017 Mar;82(3):573-584. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.13631. Epub 2017 Jan 30. J Food Sci. 2017. PMID: 28135406 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploration of Cytochrome P450-Related Interactions between Aflatoxin B1 and Tiamulin in Broiler Chickens.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Mar 20;16(3):160. doi: 10.3390/toxins16030160. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38535826 Free PMC article.
-
Seasonal Diversity and Occurrence of Filamentous Fungi in Smallholder Dairy Cattle Feeds and Feedstuffs in South Africa.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Nov 11;8(11):1192. doi: 10.3390/jof8111192. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36422014 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging mycotoxin occurrence in chicken feed and eggs from Algeria.Mycotoxin Res. 2024 Aug;40(3):447-456. doi: 10.1007/s12550-024-00537-2. Epub 2024 May 16. Mycotoxin Res. 2024. PMID: 38753281 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Aflatoxigenic Fungi in Dairy Cattle Feed: Findings From Urban Districts of Tigray, Ethiopia.Vet Med Sci. 2025 May;11(3):e70362. doi: 10.1002/vms3.70362. Vet Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40323976 Free PMC article.
-
Destruction of Mycotoxins in Poultry Waste under Anaerobic Conditions within Methanogenesis Catalyzed by Artificial Microbial Consortia.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Mar 7;15(3):205. doi: 10.3390/toxins15030205. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36977096 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wijayawardene N., Hyde K.D., Al-Ani L.K.T., Tedersoo L., Haelewaters D., Rajeshkumar K.C., Goto B.T., Saxena R.K., Aptroot A., da Silva G.A., et al. Outline of Fungi and fungus-like taxa. Mycosphere. 2020;11:1060–1456. doi: 10.5943/mycosphere/11/1/8. - DOI
-
- Moore D., Robson G.D., Trinci A.P.J. 21st Century Guidebook to Fungi. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, UK: 2011.
-
- Abdel-Azeem A.M., Abo Nahas H.H., Abdel-Azeem M.A., Tariq F.J., Yadav A.N. Biodiversity and Ecological Perspective of Industrially Important Fungi An Introduction. In: Abdel-Azeem A.M., Yadav A.N., Yadav N., Usmani Z., editors. Industrially Important Fungi for Sustainable Development. Fungal Biology. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2021. pp. 1–34.
-
- Abdelmotilib N.M., Darwish A.G., Abdel-Azeem A.M., Sheir D.H. Fungal Mycotoxins. In: Dai X., Sharma M., Chen J., editors. Fungi in Sustainable Food Production. Fungal Biology. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources