Recovery of the N,N-Dibutylimidazolium Chloride Ionic Liquid from Aqueous Solutions by Electrodialysis Method
- PMID: 35742912
- PMCID: PMC9224464
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23126472
Recovery of the N,N-Dibutylimidazolium Chloride Ionic Liquid from Aqueous Solutions by Electrodialysis Method
Abstract
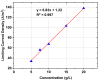
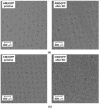
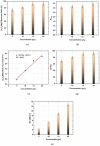
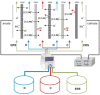
Ionic liquids (ILs), named also as liquid salts, are compounds that have unique properties and molecular architecture. ILs are used in various industries; however, due to their toxicity, the ILs' recovery from the postreaction solutions is also a very important issue. In this paper, the possibility of 1,3-dialkylimidazolium IL, especially the N,N-dibutylimidazolium chloride ([C4C4IM]Cl) recovery by using the electrodialysis (ED) method was investigated. The influence of [C4C4IM]Cl concentration in diluate solution on the ED efficiency was determined. Moreover, the influence of IL on the ion-exchange membranes' morphology was examined. The recovery of [C4C4IM]Cl, the [C4C4IM]Cl flux across membranes, the [C4C4IM]Cl concentration degree, the energy consumption, and the current efficiency were determined. The results showed that the ED allows for the [C4C4IM]Cl recovery and concentration from dilute solutions. It was found that the [C4C4IM]Cl content in the concentrates after ED was above three times higher than in the initial diluate solutions. It was noted that the ED of solutions containing 5-20 g/L [C4C4IM]Cl allows for ILs recovery in the range of 73.77-92.45% with current efficiency from 68.66% to 92.99%. The [C4C4IM]Cl recovery depended upon the initial [C4C4IM]Cl concentration in the working solution. The highest [C4C4IM]Cl recovery (92.45%) and ED efficiency (92.99%) were obtained when the [C4C4IM]Cl content in the diluate solution was equal 20 g/L. Presented results proved that ED can be an interesting and effective method for the [C4C4IM]Cl recovery from the dilute aqueous solutions.
Keywords: 1,3-dialkylimidazolium ionic liquids; N,N-dibutylimidazolium chloride; electrodialysis; ionic liquids recovery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Study on the Effectiveness of Simultaneous Recovery and Concentration of 1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium Chloride Ionic Liquid by Electrodialysis with Heterogeneous Ion-Exchange Membranes.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 1;22(23):13014. doi: 10.3390/ijms222313014. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884819 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hydrogen sulfate recovery from wastewater by electrodialysis with heterogeneous ion-exchange membranes.Sci Rep. 2025 Jun 2;15(1):19299. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-04108-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40456824 Free PMC article.
-
Electrodialysis for the Concentration of Lithium-Containing Brines-An Investigation on the Applicability.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Nov 15;12(11):1142. doi: 10.3390/membranes12111142. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36422134 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of ionic liquids in biphasic separation: Aqueous biphasic systems and liquid-liquid equilibria.J Chromatogr A. 2018 Jul 20;1559:44-61. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2017.10.019. Epub 2017 Oct 10. J Chromatogr A. 2018. PMID: 29054438 Review.
-
Aqueous ionic liquids influence the disulfide bond isoform equilibrium in conotoxin AuIB: a consequence of the Hofmeister effect?Biophys Rev. 2018 Jun;10(3):769-780. doi: 10.1007/s12551-017-0391-2. Epub 2018 Jan 2. Biophys Rev. 2018. PMID: 29294259 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in Synthesis, Characterization and Applications of Innovative Materials in Removal of Water Contaminants.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 25;24(1):330. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010330. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613774 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mai N.L., Ahn K., Koo Y.-M. Methods for recovery of ionic liquids—A review. Process Biochem. 2014;49:872–881. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2014.01.016. - DOI
-
- Feng R., Zhao D., Guo Y. Revisiting Characteristics of Ionic Liquids: A Review for Further Application Development. J. Environ. Prot. 2010;1:95–104. doi: 10.4236/jep.2010.12012. - DOI
-
- Goutham R., Rohit P., Vigneshwar S.S., Swetha A., Arun J., Gopinath K.P., Pugazhendhi A. Ionic liquids in wastewater treatment: A review on pollutant removal and degradation, recovery of ionic liquids, economics and future perspectives. J. Mol. Liq. 2022;349:118150. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2021.118150. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

